One of the underlying ideas in community detection and most of the applications outlined above is that nodes belonging to the same community share some properties. This can be used to make predictions, based on the community structure of the graph. Let's start with the subgraph illustrated in the following figure:
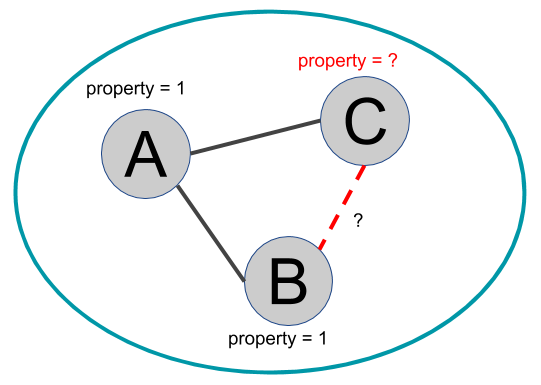
It contains three nodes, A, B and C, and two edges ((A, B) and (A, C)). This could be a part of a larger graph with more outgoing edges. Nodes A and B have a property whose value is 1. That could be the age category of some users, which is not always available. Users A and B have filled that field, indicating they are between 21 and 30. On top of that, some community detection algorithms have managed to cluster all three nodes into the same community. Intuitively, we can say that the probability of node C also falling into the 21-30 age category increases with this new knowledge about the graph structure.
Similarly, if we try to measure...
































































