In Dijkstra's algorithm, all possible paths are explored. This can be very time-consuming, especially on large graphs. The A* algorithm tries to overcome this problem, with the idea that it can guess which paths to follow and which path expansions are less likely to be the shortest ones. This is achieved by modifying the criterion for choosing the next start node at each iteration. Instead of using only the cost of the path from the start to the current node, the A* algorithm adds another component: the estimated cost of going from the current node to the end node. It can be expressed as follows:
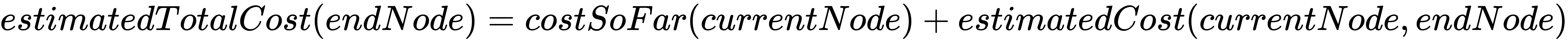
While costSoFar(currentNode) is the same as the one computed in Dijkstra's algorithm, estimatedCost(currentNode, endNode) is a guess about the remaining cost of going from the current node to the end node. The guess function, often noted as h, is a heuristic function.
































































