Spatial indexes, like any other indexes, are a way of running spatial queries much faster by avoiding having to perform the most complex operations on all the entities. For instance, let's consider the intersection query, where we're trying to find the points intersecting a complex polygon, similar to the one illustrated in the following diagram:
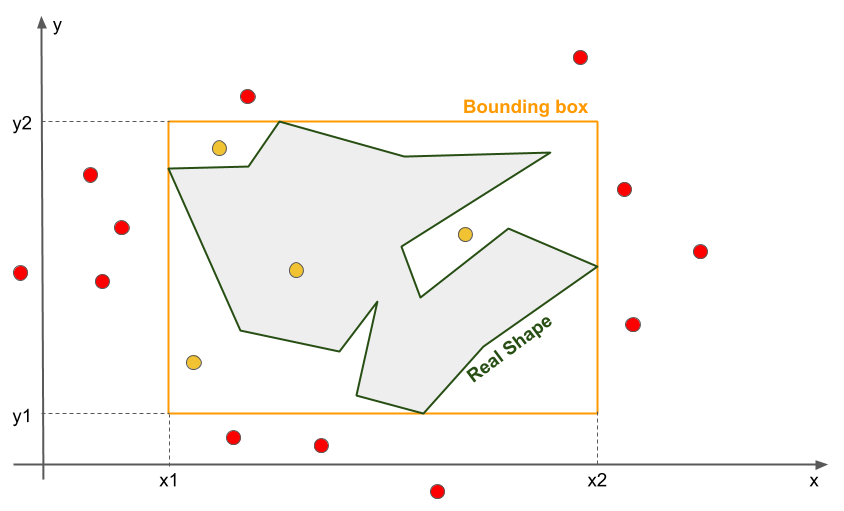
The rules of deciding whether points lie within the real shape are quite complex. However, it is straightforward to decide whether the same points are within the rectangle drawn around the complex area: we just have to perform four comparisons:
x1 < x < x2
and y1 < y < y2
Only the points fulfilling this condition will be tested in order to decide whether they belong to the real shape Doing this usually reduces the number of (complex) operations to be performed considerably.
The rectangle drawn around the real shape is called the bounding box of the real shape. It is the smaller rectangle containing...
































































