Let's briefly focus on relational databases. Imagine we want to create a Question and Answer website (similar to the invaluable Stack Overflow). The requirements are the following:
- Users should be able to log in.
- Once logged in, users can post questions.
- Users can post answers to existing questions.
- Questions need to have tags to better identify which question is relevant for which user.
As developers or data scientists, who are used to SQL, we would then naturally start thinking in terms of tables. Which table(s) should I create to store this data? Well, first we will look for entities that seem to be the core of the business. In this QA website, we can identify the following:
- Users, with attributes: ID, name, email, password
- Questions: ID, title, text
- Answers: ID, text
- Tags: ID, text
With those entities, we now need to create the relationships between them. To do so, we can use foreign keys. For instance, the question has been asked by a given user, so we can just add a new column to the question table, author_id, referencing the user table. The same applies for the answers: they are written by a given user, so we add an author_id column to the Answer table:
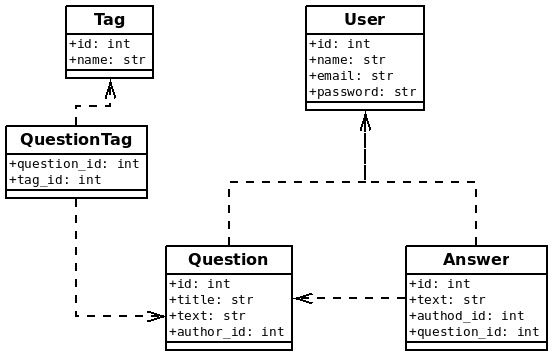
It becomes more complicated for tags, since one question can have multiple tags and a single tag can be assigned to many questions. We are in the many-to-many relationship type, which requires adding a join table, a table that is just there to remember that kind of relationship. This is the case of the QuestionTag table in the preceding diagram; it just holds the relationship between tags and questions.

































































