Passing arguments to WPF applications
The command-line arguments are used to take optional parameters or values from the user, while launching the application. These are generally used to perform specific commands on the application from the outside.
In this recipe, we will learn how to pass command-line arguments to a WPF application.
Getting ready
To get started, open the Visual Studio IDE and create a WPF application project called CH01.CommandLineArgumentDemo.
How to do it...
Now follow these steps to let the application support command line arguments and perform actions based on those:
- Open the
MainWindow.xamlto add aTextBlockinto theGridpanel. Replace the entire XAML content with the following lines:
<Window x:Class="CH01.CommandLineArgumentDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns=
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Main Window" Height="200" Width="400">
<Grid>
<TextBlock Text="This is 'Main Window'
of the application."
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
FontSize="18" />
</Grid>
</Window> - Create a new window in the project by right-clicking on the project node and then following the context menu path
Add|Window...to open theAdd New Itemdialog window. Give it the nameOtherWindowand click theAddbutton. This will addOtherWindow.xamlandOtherWindow.xaml.csinto the project.
- Now open the
OtherWindow.xamland change its UI to have different text. Let's replace the entire XAML code with the following lines:
<Window x:Class="CH01.CommandLineArgumentDemo.OtherWindow"
xmlns=
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Other Window" Height="200" Width="400">
<Grid>
<TextBlock Text="This is 'Other Window' of the
application."
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
FontSize="18" />
</Grid>
</Window> - Now open the
App.xamland remove theStartupUri="MainWindow.xaml". This has been done to control the launch of the proper window, based on the argument passed to the application. - Open the
App.xaml.csand override itsOnStartupmethod to retrieve the arguments passed to it and open the desired window based on that. Let's add the following code implementation for theOnStartupmethod:
protected override void OnStartup(StartupEventArgs e)
{
base.OnStartup(e);
var args = e.Args;
if (args.Contains("/other"))
{
new OtherWindow().Show();
}
else
{
new MainWindow().Show();
}
} - Now build the project. Navigate to the
bin\Debugfolder and launch aCommand Windowin that location. Alternatively, you can launch a Command Window (cmd.exe) and navigate to thebin\Debugpath, where your application is available.
- In the console window, enter the name of the application without passing any arguments to it, as shown in the following command:
CH01.CommandLineArgumentDemo.exe- This will launch the
MainWindowof our application, with this screen: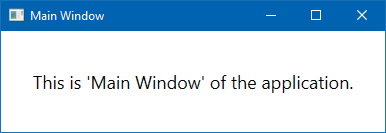
- Close the application window and, from the console window, enter the application name by specifying the
/otherargument to it, as shown in the following command:
CH01.CommandLineArgumentDemo.exe /other- This will launch the
OtherWindowof the application, instead of theMainWindow: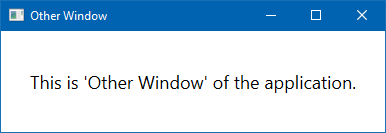
How it works...
The OnStartup(StartupEventArgs e) method signature contains StartupEventArgs as a method parameter. It contains a property, Args, that returns a string array of the command line arguments that were passed to the application. If no command line arguments were passed, the string array will have zero items in it.
Now, by checking the condition, we launch the desired window that we want to show to the user. You can also take arguments such that the application launches in normal mode, maximized mode, or minimized. You can also use it to open the application as hidden, in some specific cases.
There's more...
As we have seen how to launch the WPF application from the command line by passing the arguments, let's learn how to do this from Visual Studio itself to launch it in debug mode.
To pass a command line argument to your WPF application from Visual Studio in debug mode, right-click on the project node and click Properties from the context menu entry. This will open the project properties. Now navigate to the Debug tab. Please refer to the following screenshot:
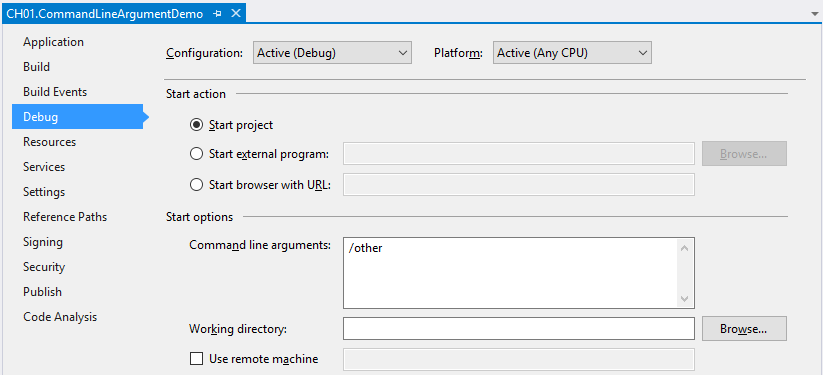
Under Start options, enter /other as the command line arguments. Now run the application in debug mode by pressing F5. You will see that the OtherWindow opens on the screen. To launch the MainWindow, just remove the /other argument from the project properties mentioned earlier and run the application again. This time you will see that the MainWindow opens instead of the OtherWindow.

































































