DHCP attacks
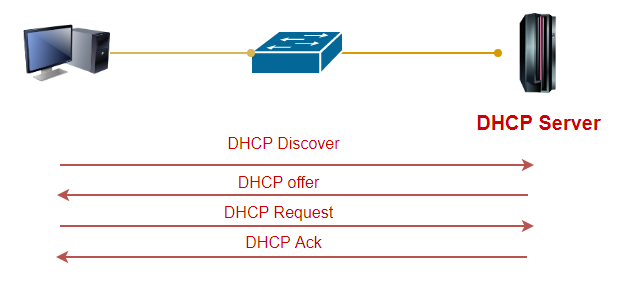
DHCP is a network layer protocol based on RFC 2131 that enables assigning IP addresses dynamically to hosts. The following four required steps to assign an IP address to a specific host:
- DHCP discover
- DHCP offer
- DHCP request
- DHCP acknowledgment
DHCP starvation
In this chapter, we are discussing layer 2 attacks; I bet you are wondering why we talked about a network layer protocol (DHCP in our case). The answer is easy. Attackers can perform what we call DHCP starvation. An attacker broadcasts DHCP requests with spoofed MAC addresses; this attack exploits the DHCP servers address space. This attack can be done using a simple tools, such as the gobbler.
Rogue DHCP server
A rogue DHCP server (this can be a home router or a modem) is a server implemented by an attacker in a network to perform man-in-the-middle attacks, or sniffing the network traffic. This implementation of a rogue server lets the attacker gather a great deal of information, including DNS server information and the default...





































































