Adaptive boosting
Schapire and Freund invented the adaptive boosting method. Adaboost is a popular abbreviation of this technique.
The generic adaptive boosting algorithm is as follows:
Initialize the observation weights uniformly:
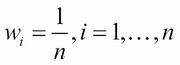
For m, classifier hm, from 1 to m number of passes over with the data, perform the following tasks:
-
Fit a classifier hm to the training data using the weights
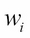
Compute the error for each classifier as follows:
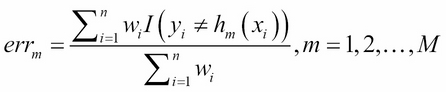
Compute the voting power of the classifier hm:
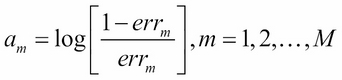
-
Set
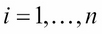
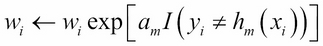
-
Fit a classifier hm to the training data using the weights
Output:
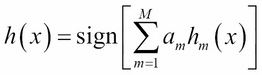
Simply put, the algorithm unfolds as follows:
-
Initially, we start with uniform weights
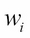 for all observations.
for all observations.
-
In the next step, we calculate the weighted error
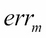 for each of the classifiers under consideration.
for each of the classifiers under consideration.
A classifier (usually stumps, or decision trees with a single split) needs to be selected and the practice is to select the classifier with the maximum accuracy.
In Improve distribution and Combine outputs case of ties, any accuracy tied classifier is selected.
Next, the misclassified observations...







































































