Using modular inputs
Since Splunk 5.0, the ability to extend data input functionality has existed such that custom input types can be created and shared while still allowing for user customization to meet needs.
Modular inputs build further upon the scripted input model. Originally, any additional functionality required by the user had to be contained within a script. However, this presented a challenge, as no customization of this script could occur from within Splunk itself. For example, pulling data from a source for two different usernames needed two copies of a script or meant playing around with command-line arguments within your scripted input configuration.
By leveraging the modular input capabilities, developers are now able to encapsulate their code into a reusable app that exposes parameters in Splunk and allows for configuration through processes familiar to Splunk administrators.
This recipe will walk you through how to install the Command Modular Input, which allows for periodic execution of commands and subsequent indexing of the command output. You will configure the input to collect the data outputted by the vmstat command in Linux and the systeminfo command in Windows.
Getting ready
To step through this recipe, you will need a running Splunk server with a connection to the internet. No other prerequisites are required.
You will also need to download the Command Modular Input Add-on app from Splunkbase. This app can be found at https://splunkbase.splunk.com/app/1553/.
How to do it...
Follow the steps in this recipe to configure a modular input:
- Log in to your Splunk server.
- From the
Appsmenu in the upper left-hand corner of the home screen, click on the gear icon:
- The
Apps settingspage will load. Then, click on theInstall App from filebutton. - Click the
Choose Filebutton and select the app file that was previously downloaded from Splunkbase, then click theUploadbutton: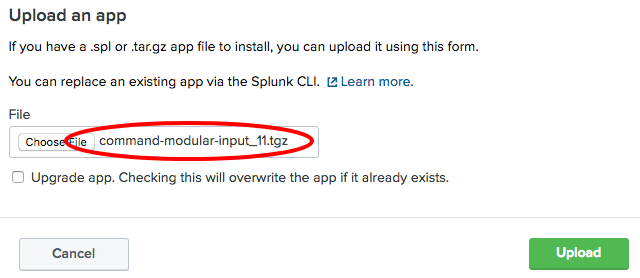
- After the app has been installed, from the menu in the top right-hand corner, click on the
Settingsmenu and then click on theData inputslink. - Click on the
Commandsection:
- In the
Mod Input Namefield, enter a name for the input ofSystemInfo. If you are using Linux, enter/usr/bin/vmstatin theCommand Namefield. If you are using Windows, enterC:\Windows\System32\systeminfo.exein theCommand Namefield: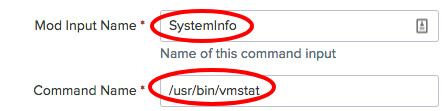
Note
Usethe full path if the command to be executed cannot be found on the system PATH.
- In the
Command Argumentsfield, enter any argument that needs to be passed to the command listed in theCommand Namefield. In theCommand Execution Intervalfield, enter a value in seconds for how often the command should be executed (in this case, we will use 60 seconds). If the output is streamed, then leave this field empty and check theStreaming Outputfield: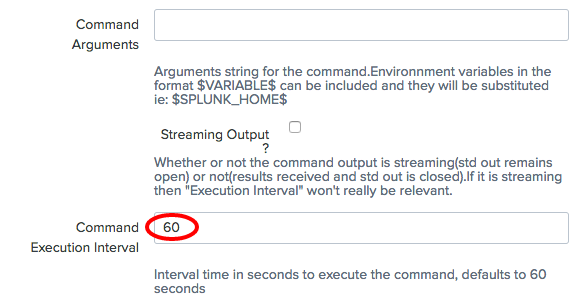
- In the
Source typesection, you have the option to either select a predefined source type or selectManualand enter a value. For this recipe, selectManualas the source type and entercp01_modular_inputas the value for the source type. - Click
Next. - If everything was successful, you should see a
Modular input has been created successfullymessage:
- Click on the
Start searchingbutton. TheSearch & Reportingapp will open with the search already populated based on the settings supplied earlier in the recipe. Splunk is now configured to execute the modular input you provided, every 60 seconds, in accordance with the specified interval. You can search for this data returned by the scripted input using the following search over anAll timetime range:
sourcetype=cp01_modular_input
How it works...
Modular inputs are bundled as Splunk apps and, once installed, contain all the necessary configuration and code to display them in the Data inputs section of Splunk. In this recipe, you installed a modular input application that allows for periodic execution of commands. You configured the command to execute every minute and to index the results of the command each time, giving the results a source type of cp01_modular_input.
Modular inputs can be written in several languages and need to follow only a set of interfaces that expose the configuration options and runtime behaviors. Depending on the design of the input, they will either run persistently or run at an interval and will send data to Splunk as they receive it.
Note
You can find several other modular inputs, including REST API, SNMP, and PowerShell, on the Splunk Apps site (https://splunkbase.splunk.com).
There's more...
To learn how to create your own modular input, refer to the Modular Inputs section of the Developing Views and Apps for Splunk web manual located at https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/AdvancedDev/ModInputsIntro.
See also
- The Indexing files and directories recipe
- The Getting data through network ports recipe
- The Using scripted inputs recipe































































