Receiving data using the HTTP Event Collector
The HTTP Event Collector (HEC) is another highly scalable way of getting data into Splunk. The HEC listens for HTTP requests containing JSON objects and sends the data that has been collected to be indexed.
In this recipe, you will learn how to configure the Splunk HTTP Event Collector to receive data coming from an example Inventory Scanner. This example inventory scan HEC configuration will be used in Chapter 10, Above and Beyond – Customization, Web Framework, REST API, HTTP Event Collector, and SDKs.
Getting ready
To step through this recipe, you will need a running Splunk Enterprise server. You should be familiar with navigating the Splunk user interface and using the Splunk search language. This recipe will use the open source command-line tool, curl. There are other command-line tools available, such as wget. The curl tool is usually installed by default on most Mac and Linux systems but can be downloaded for Windows systems as well.
Note
For more information on curl, visit http://curl.haxx.se/.
How to do it...
Perform these steps to create a custom search command to format product names:
- Log in to your Splunk server.
- Select the
Search & Reportingapplication. - Click on
Settingsand then onData Inputs: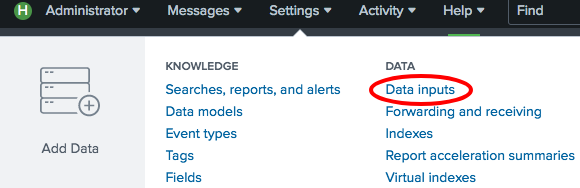
- Click on
HTTP Event Collector: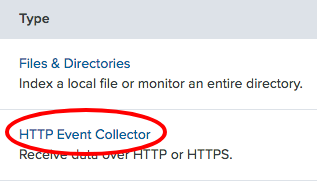
- Click the
Global Settingsbutton: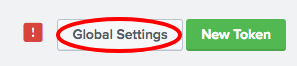
- Set
All TokenstoEnabled, and set theDefaultIndextomain. Then, click theSavebutton: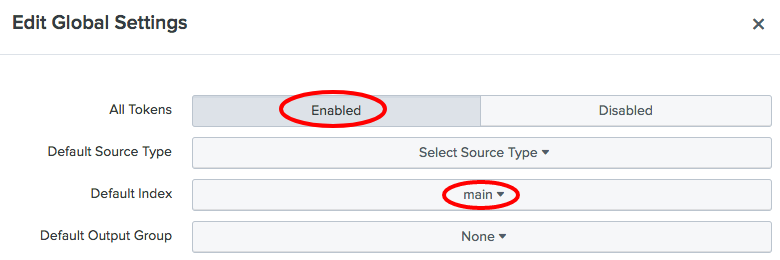
- Click the
New Tokenbutton:
- Set the
NametoInventory Scannerand theSource name overridetoinventory:scanner, and click theNextbutton: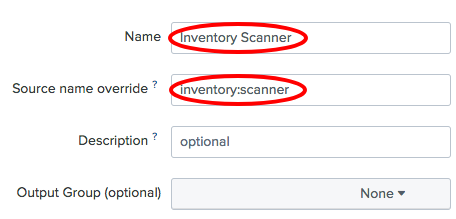
- Select
Newfor theSource Typeand enterinventory:scanneras the value: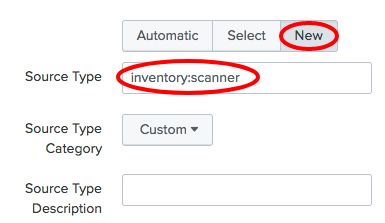
- Under the Index section, click on
mainso that it gets moved to theSelectedItem(s)list and click theReviewbutton: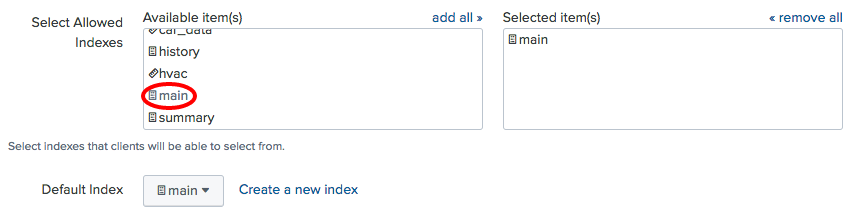
- Click
Reviewand confirm your selections, then clickSubmit. - After the form submits, you will be presented with the token. This token will be needed for the recipe in Chapter 10, Above and Beyond – Customization, Web Framework, REST API, HTTP Event Collector, and SDKs:
How it works...
To get the HEC to work, you firstly configured a few global settings. These included the default index, default source type, and the HTTP port that Splunk will listen on. These default values, such as index and source type, will be used by the HEC, unless the data itself contains the specific values to use. The port commonly used for the HEC is port 8088. This single port can receive multiple different types of data since it is all differentiated by the token that is passed with it and by interpreting the data within the payload of the request.
After configuring the defaults, you then generated a new token, specifically for the inventory scanner data. You provided a specific source type for this data source and selected the index that the data should go to. These values will override the defaults and help to ensure that data is routed to the correct index.
The HEC is now up and running and listening on port 8088 for the inventory scan HTTP data to be sent to it.































































