The silhouette coefficient finds the similarity of an item in a cluster to its own cluster items and other nearest clusters. It is also used to find the number of clusters, as we have seen elsewhere in this chapter. A high silhouette coefficient means better clustering results. This can be calculated as follows:
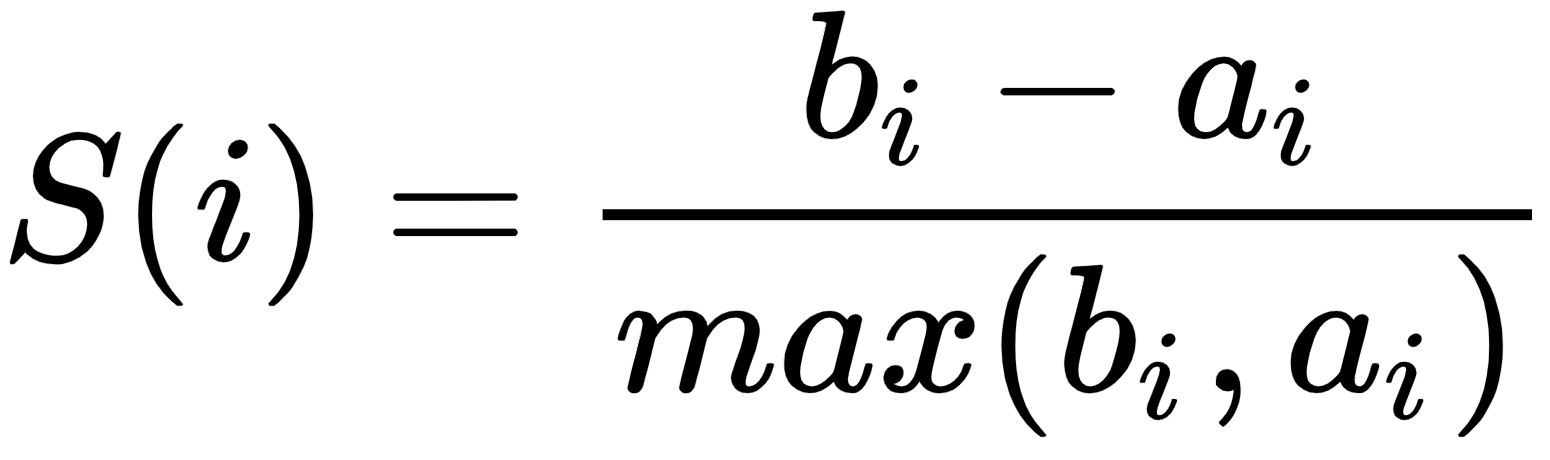
ai is the average distance of the ith data point to other points within the cluster.
bi is the average distance of the ith data point to other cluster points.
So, we can say that S(i) would be between [-1, 1]. So, for S(i) to be near to 1, ai must be very small compared to bi, that is, ai << bi.






































































