The example application
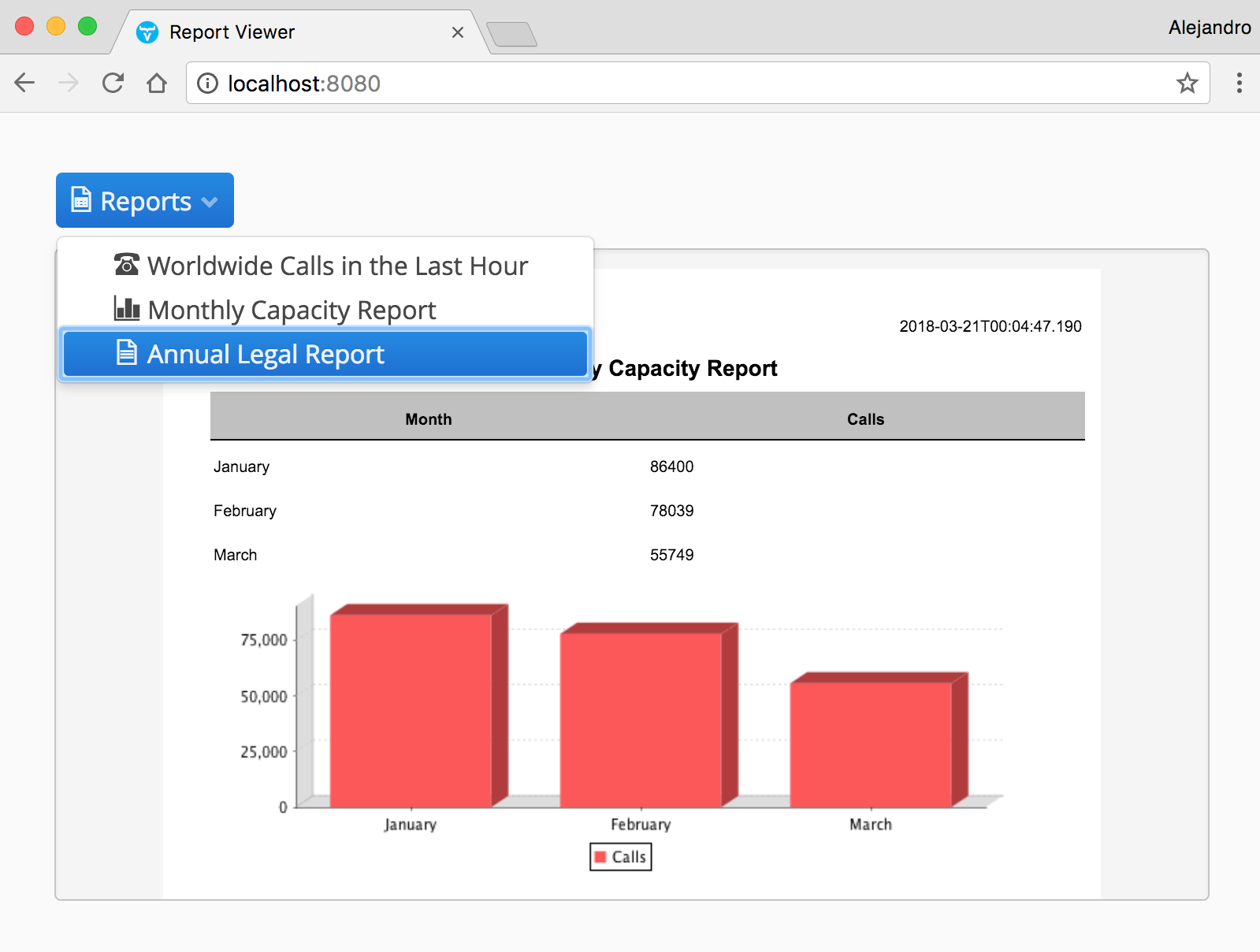
Throughout the chapter, we'll develop a Report Viewer. The following is a screenshot of the finished application:
The data model
The data model is based on a simple SQL table, Call, that contains columns for the ID, client name, phone number, city, start time, duration, and status. The following is a JPA Entity representing this table:
@Entity
@Data
public class Call {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String client;
private String phoneNumber;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private City city;
private LocalDateTime startTime;
private Integer duration;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private Status status;
}Status and City are simple Java enums that define some test values:
public enum Status { RECEIVED, MISSED } public enum City { BOGOTA, TURKU, LONDON, BERLIN, HELSINKI, TOKYO, SAN_FRANCISCO, SIDNEY, LAGOS, VANCOUVER, SANTIAGO, BEIJING }
Notice the @Enumerated annotations in the city and status fields of the Call class. This is used to persist the...



























































