The Intelligence Cycle
Before diving into the theory of the intelligence cycle, I believe it is worth showing the relationship between data, knowledge and intelligence practice through what is known as a knowledge pyramid. In it we can see how the facts, through measurement, are transformed into data from which we extract information when processing them and that when analyzed together we transform into knowledge. This knowledge interacts with our own experience and forms the basis of what we call wisdom. It is this ultimate wisdom that we rely on for decision making.
As we can see in the pyramid shown below, we can intertwine this knowledge pyramid with the processes that are part of what is widely known as The Intelligence Cycle.
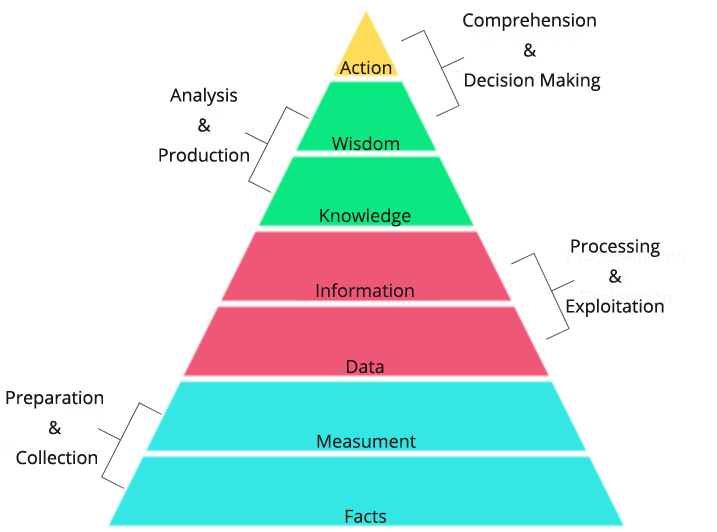
In short, we can deduce from here that an intelligence analyst must process data to transform it into wisdom (intelligence) that in the last instance would lead to an action (decision).
Traditionally, the intelligence process is understood as a six-phase cycle: planning and targeting, preparation and collection, processing and exploitation, analysis and production, dissemination and integration, evaluation and feedback. Each of these phases presents its own particularities and challenges.
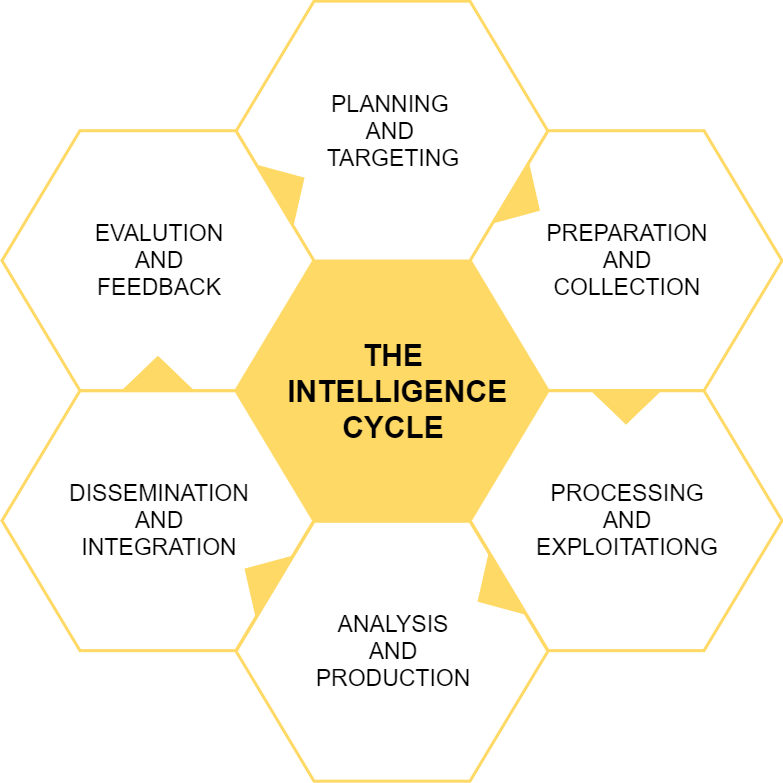
Planning and targeting
The first step is to identify the intelligence requirements (IRs). It will fall under this category any information that the decision makers need and don’t know enough about.
In this stage of the process it is important to identify the key assets of the organization, why the organization might be an interesting target and what are the security concerns of those in charge of making decisions.
It’s also important to identify which are the potential threats that exist and what mitigations can be prioritized (process known as threat modeling), as well as establishing a collection framework and collection priorities.
Preparation and collection
This stage refers to the definition and development of collection methods to obtain information regarding the requirements established in the previous phase.
It is important to keep in mind that it’s impossible to answer all the questions we may have, as well as it is also impossible to meet all the Intelligence Requirements.
Processing and exploitation
Once the planned data has been collected, the next step is to process it to generate information. The processing method is usually not perfect and the amount of data that the intelligence team is able to process is always lower than the amount of data that is able to gather. All data that does not get processed, is the same as data not collected at all. It is intelligence lost.
Analysis and production
The information gathered must be analyzed in order to generate intelligence. There are several techniques used for intelligence analysis and avoid analyst bias. The cyber threat intelligence analyst must learn how to filter his personal views and opinions to do the analysis.
Dissemination and integration
In this stage the distribution of intelligence produced to the necessary sectors occurs. Before distribution the analysts have to consider a variety of things like what are the most pressing issues among the intelligence collected, who should receive the report, how urgent the intelligence is or how much detail does the recipient need, should or shouldn’t the report include preventive recommendations... Sometimes, even the creation of different reports directed to different audiences might be needed.
Evaluation and feedback
This consists of the final stage of the process and probably the most difficult to achieve, mainly due to the usual lack of feedback from the intelligence recipients. Establishing good mechanisms to get feedback would help intelligence producers evaluate the effectiveness of the intelligence generated before repeating the process making the necessary adjustments.
This model has been widely accepted and adopted, especially in the United States of America and among those who follow their academic discussions in an attempt to replicate its methods. Despite this wide acceptance, there have been some vocal criticisms against this model.
Some have pointed out that the current model depends excessively on the data collected and that the technological advanced has allowed us to collect massive amounts of it. This endless harvesting process and the capacity to better represent the data collected, leads us to believe that that this process itself it is enough to understand what is happening.
There have been alternative proposals for the intelligence cycle described before. For anyone interested in study more on the matter, there is a particularly interesting contribution on the matter published by Davies, Gustafson and Ridgen (2013) titled “The Intelligence Cycle is Dead, Long Live the Intelligence Cycle: Rethinking Intelligence Fundamentals for a New Intelligence Doctrine” (https://bura.brunel.ac.uk/bitstream/2438/11901/3/Fulltext.pdf), in which what has been labeled as “the UK Intelligence Cycle” was described in detail.
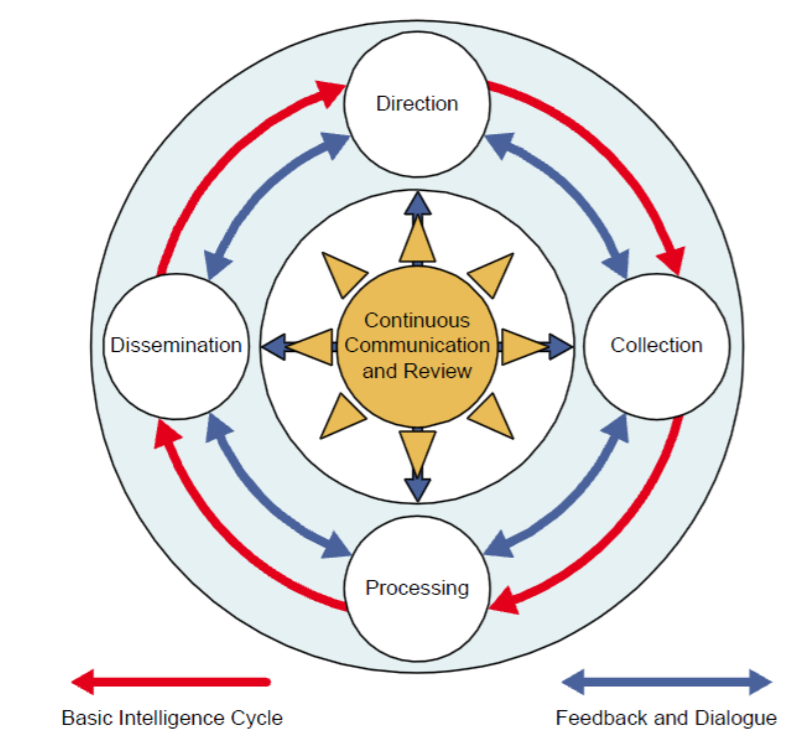
[…]





































































