Using the asyncio event loop and coroutine scheduler
So far, you have learned about Python's coroutines and a bit about how a cooperative coroutine scheduler works. Now, let's try our hand at writing some asynchronous code using Python coroutines and asyncio. We start this by creating a coroutine.
Creating a coroutine
It's easy to create a coroutineâall we have to do is use the async keyword on a function and use await anytime we want to call other coroutines, as shown in following code example:
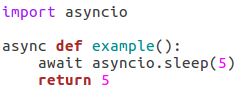
Once we have a coroutine though, we can't just call it to get the ball rolling. If we try to call it, it immediately returns a coroutine object, as shown in the following code exampleâthat's not much use:
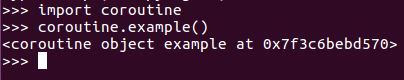
Instead, we need to add the coroutine to the asyncio's scheduler as a new task. Next, the scheduler runs arranging for coroutines to execute and handling input and output events.
The asyncio scheduler - event_loop
The asyncio package automatically creates a default scheduler, also called event_loop...




































































