Exploiting routing protocols
In this section, we will explore many routing protocols and how to exploit each one of them, and we will learn the required defenses to protect your network.
Routing Information Protocol
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) v1 is a distance vector protocol. It sends a routing table every 30 seconds. RIP uses the hop count as a decision metric. This is an old protocol, and it can't reach more than 15 hops in its first version, RIPv1. To reach a destination, RIP uses the path with the lowest number of hops, but this is not that efficient because in some cases, there are many routes with more hop counts but with better bandwidth. For example, in the following network when using RIPv1, the traffic will be forwarded via Route 1, and even Route 2 has a greater bandwidth:
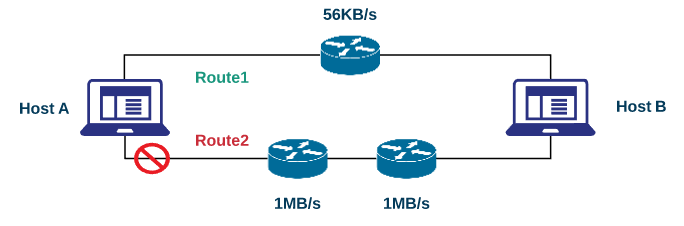
Many revisions are taken into consideration in the successor of RIPv1. RIPv2 is an enhanced version of RIPv1. Although RIP is a classful routing protocol, RIPv2 is classless, which means it includes the...





































































