Interrupt request and propagation
Let us consider the following diagram, which represents a chained IRQ flow:
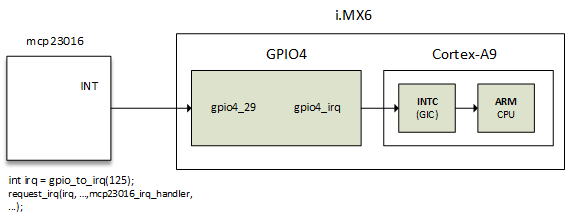
Interrupt requests are always performed on a Linux IRQ (not hwirq). The general function to request an IRQ on Linux is either request_threaded_irq() or request_irq(), which internally calls the former:
int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,
const char *devname, void *dev_id) When called, the function extracts the struct irq_desc associated with the IRQ, using the irq_to_desc() macro. It then allocates a new struct irqaction structure and sets it up, filling parameters such as the handler, the flags, and so on:
action->handler = handler; action->thread_fn = thread_fn; action->flags = irqflags; action->name = devname; action->dev_id = dev_id;
That same function inserts/registers the descriptor in the proper IRQ list by invoking the __setup_irq() function...

































































