Activation functions
The output from the neuron is computed as shown in Figure 3, and passed through an activation function that introduces non-linearity to the output. This f is called an activation function. The main purposes of the activation functions are to:
- Introduce nonlinearity into the output of a neuron. This is important because most real-world data is nonlinear and we want neurons to learn these nonlinear representations.
- Squash the output to be in a specific range.
Every activation function (or nonlinearity) takes a single number and performs a certain fixed mathematical operation on it. There are several activation functions you may encounter in practice.
So, we are going to briefly cover the most common activation functions.
Sigmoid
Historically, the sigmoid activation function is widely used among researchers. This function accepts a real-valued input and squashes it to a range between 0 and 1, as shown in the following figure:
σ(x) = 1 / (1 + exp(−x))
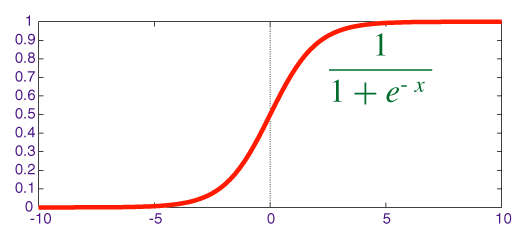
Figure 4: Sigmoid activation...






































































