Using function decorators
In this section, we're going to look at one of the most ubiquitous function decorators. We'll see how to construct a decorator, how to use it, and how it works.
The basic definition of a decorator is simple. It's just a function that takes another function as its input, does something with it, and then returns the result of its operations, as shown here:
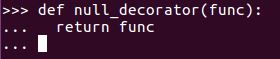
The return value replaces the original input function, so the changes a decorator can make are potentially quite drastic. A decorator that doesn't change anything at all is a function that accepts one parameter and immediately returns it.
Using the @ syntax in a function decorator
Python has a special syntax for applying a decorator to a function, using the @ syntax. With this syntax, we just write an @ symbol, followed by an expression that evaluates to a decorator function. We put that on the line right before the definition of the function we want to decorate, as shown in the following code example:
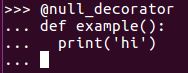
This syntax means...




































































