Using scripted inputs
Not all data that is useful for operational intelligence comes from logfiles or network ports. Splunk will happily take the output of a command or script and index it along with all your other data.
Scripted inputs are a very helpful way to get that hard-to-reach data. For example, if you have third-party-supplied command-line programs that can output data you would like to collect, Splunk can run the command periodically and index the results. Typically, scripted inputs are often used to pull data from a source, whereas network inputs await a push of data from a source.
This recipe will show you how to configure Splunk on an interval to execute your command and direct the output into Splunk.
Getting ready
To step through this recipe, you will need a running Splunk server and the provided scripted input script suited to the environment you are using. For example, if you are using Windows, use the cp01_scripted_input.bat file. This script should be placed in the $SPLUNK_HOME/bin/scripts directory. No other prerequisites are required.
How to do it...
Follow these steps to configure a scripted input:
- Log in to your Splunk server.
- From the menu in the top right-hand corner, click on the
Settingsmenu and then click on theAdd Datalink. - If you are prompted to take a quick tour, click on
Skip. - In the
How do you want to add datasection, click onMonitor. - Click on the
Scriptssection: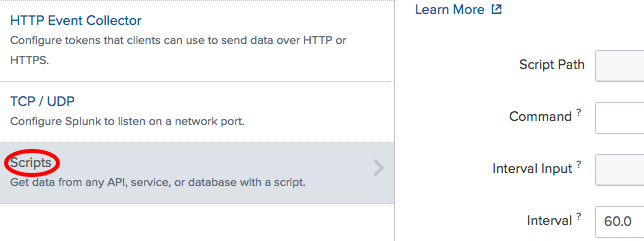
- A form will be displayed with a number of input fields. In the
Script Pathdrop-down, select the location of the script. All scripts must be located in a Splunkbindirectory, either in$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/scriptsor an appropriate bin directory within a Splunk app, such as$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/search/bin. - In the
Script Namedropdown, select the name of the script. In theCommandsfield, add any command-line arguments to the auto-populated script name.
- Enter the value in the
Intervalfield (in seconds) in which the script is to be run (the default value is60.0seconds) and then clickNext: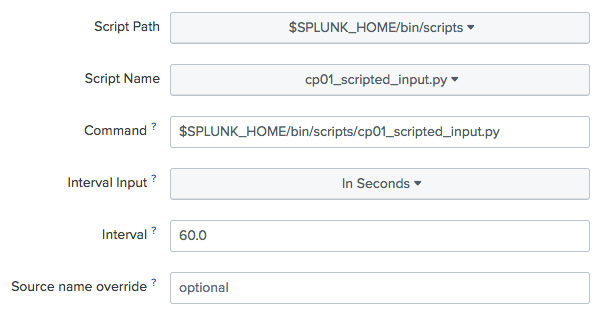
- In the
Source Typesection, you have the option to either select a predefined source type or to selectNewand enter your desired value. For the purpose of this recipe, selectNewas the source type and entercp01_scripted_inputas the value for the source type. Then clickReview: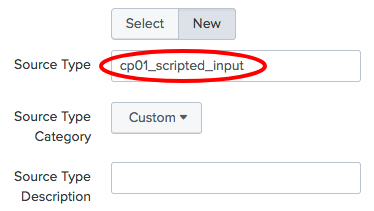
By default, data will be indexed into the Splunk index of
main. To change this destination index, select your desired index from the drop-down list in theIndexsection of the form.Review the settings. If everything is correct, click
Submit.If everything was successful, you should see a
Script input has been created successfullymessage: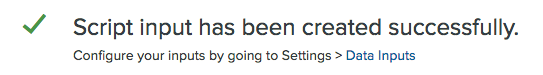
- Click on the
Start searchingbutton. TheSearch & Reportingapp will open with the search already populated based on the settings supplied earlier in the recipe. Splunk is now configured to execute the scripted input you provided every 60 seconds, in accordance with the specified interval. You can search for the data returned by the scripted input using the following search:
sourcetype=cp01_scripted_input
How it works...
When adding a new scripted input, you are directing Splunk to add a new configuration stanza into an inputs.conf file behind the scenes. The Splunk server can contain one or more inputs.conf files, located either in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local or the local directory of a Splunk app.
After creating a scripted input, Splunk sets up an internal timer and executes the command that you have specified, in accordance with the defined interval. It is important to note that Splunk will only run one instance of the script at a time, so if the script gets blocked for any reason, it will cause the script to not be executed again, until after it has been unblocked.
Since Splunk 4.2, any output of the scripted inputs that are directed to stderr (causing an error) are captured to the splunkd.log file, which can be useful when attempting to debug the execution of a script. As Splunk indexes its own data by default, you can search for that data and put an alert on it if necessary.
For security reasons, Splunk does not execute scripts located outside of the bin directories mentioned earlier. To overcome this limitation, you can use a wrapper script (such as a shell script in Linux or batch file in Windows) to call any other script located on your machine.
See also
- The Indexing files and directories recipe
- The Getting data through network ports recipe
- The Using modular inputs recipe































































