Make use of sudoers – configuring sudo access
Sudoer is the functionality of the Linux system that can be used by an administrator to provide administrative access to a trusted regular user, without actually sharing the root user's password. The administrator simply needs to add the regular user in the sudoers list.
Once a user has been added to the sudoers list, they can execute any administrative command by preceding it with sudo. Then the user would be asked to enter their own password. After this, the administrative command would be executed the same way as by the root user.
Getting ready
As the file for the configuration is pre-defined and the commands used are inbuilt, nothing extra is needed to be configured before starting the steps.
How to do it…
Perform the following steps:
- You will first create a normal account and then give it sudo access. Once done, you will be able to use the
sudocommand from the new account and then execute the administrative commands. Follow the steps given to configure sudo access. First, use the root account to log in to the system then create a user account using theuseraddcommand, as shown. ReplaceUSERNAMEin the command with any name of your choice:

- Now, using the
passwdcommand set a password for the new user account, as shown: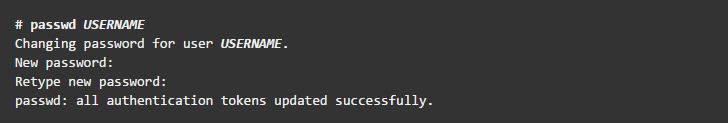
- Now edit the
/etc/sudoersfile by running thevisudoas shown. The policies applied when using thesudocommand, are defined by the/etc/sudoersfile:
- Once the file is open in the editor, search for the following lines which allow sudo access to the users in the test group:
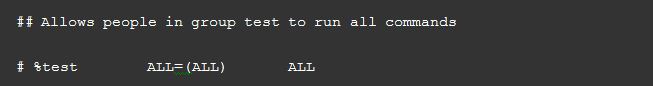
- You can enable the given configuration by deleting the comment character (
#) at the beginning of the second line. Once the changes are done, save the file and exit from the editor. Now using theusermodcommand, add the previously created user to the test group:
- Now you need to check whether the configuration created now allows the new user account to run commands using
sudo.
- To switch to the newly created user account, use the
suoption:
- Now use the
groupscommand to confirm the presence of the user account in the test group:
Finally, run the whoami command with sudo from the new account. As you have executed a command using sudo for the first time using this new user account, the default banner message will be displayed for the sudo command. The screen will also ask for the user account password to be entered:

- The last line of the output shown is the username returned by the
whoamicommand. Ifsudois configured correctly this value will be root.
You have successfully configured a user with sudo access. You can now log in to this user account and use sudo to run commands the same way as you would from the root user.
How it works…
When you create a new account, it does not have the permission to run administrator commands. However, after editing the /etc/sudoers file, and making appropriate entry to grant sudo access to the new user account, you can start using the new user account to run all administrator commands.
There’s more…
Here are some extra measures that you can take to ensure total security.
Vulnerability assessment
A vulnerability assessment is the process of auditing your network and system security, through which you can come to know about the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your network. The first phase in vulnerability assessment is reconnaissance, and this further leads to the phase of system readiness, in which we mainly check for all known vulnerabilities in the target. Next follows the phase of reporting in which we group all the vulnerabilities found into categories of low, medium, and high risk.






































































