Breadth first search
Breadth first search (BFS) is a type of traversal that focuses on visiting the nodes of the same level (or neighbors) before going deeper into the graph (to the neighbors of the neighbors).
Another condition to take into account is that we should visit each node just once. Let's see an example with the following graph:
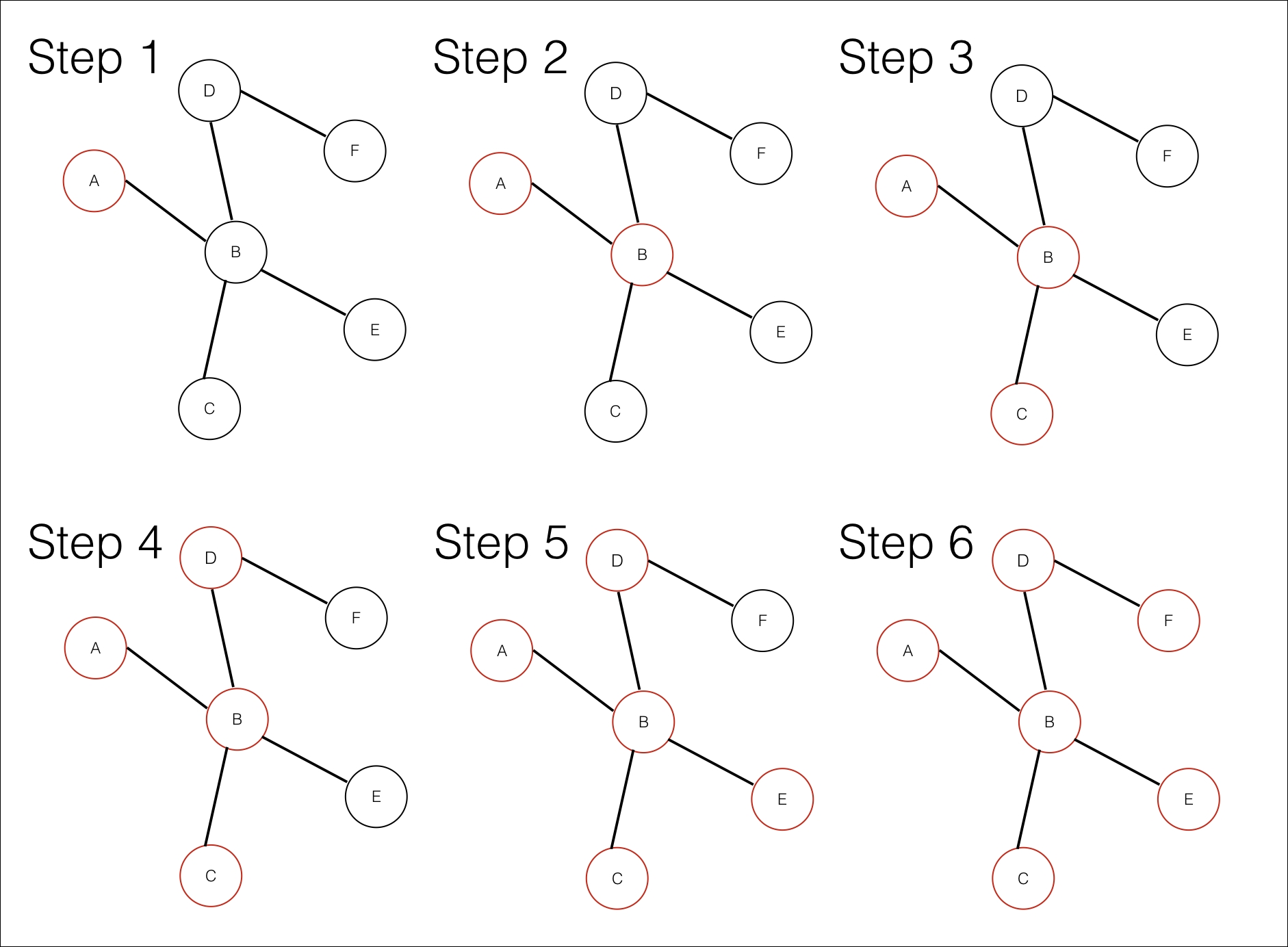
BFS example
In step 1, we visit node A. Then we pass to the first child of A: node B. We visit all the children of B: C, D, and E, before going into its grandchildren: F.
We have already implemented Vertex, Edge, and AdjacencyList structs. We are going to make an example of BFS based on a graph built with classes instead, so we will cover both approaches.
Let's start by implementing a graph node with a Swift class. In order to perform a BFS, we need a data structure that contains info about the following:
Some value to identify the node (such as in the preceding figure: A, B, C, D, and so on).
The list of connected nodes (or children, neighbors...it depends...
























































