IDS and IPS
In this section, we will discuss the difference between and the placement of both an IDS and an IPS.
Intrusion Detection Systems
An Intrusion Detection System is an appliance that is used to detect security threats, either on a host system or a network. Let's use the following network topology to further explain how an IDS works:
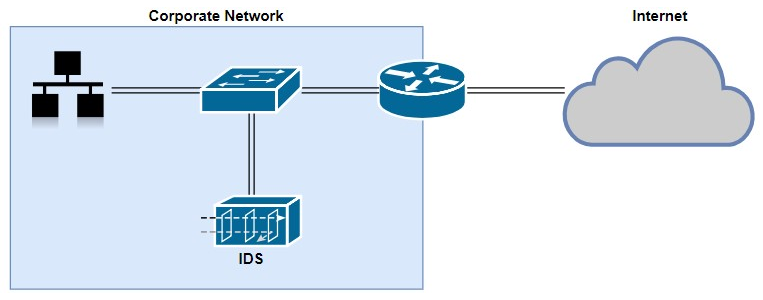
As you can see, the IDS is not connected inline but to a port on the switch; therefore, the IDS will receive a copy of the network traffic for analysis and does not add any latency or delay the flow of traffic. Furthermore, if the IDS appliance is disabled or goes down, the network performance is not impacted. However, since it receives only a copy of the traffic and it's not an inline deployment (that is, network traffic is not passing through the appliance), only after a threat has been detected, the IDS appliance will generate an alert and will not be able to stop the attack as it's happening on the network. This makes the appliance reactive rather than...




































































