Computing the coefficient of a correlation
In the Using the built-in statistics library and Average of values in a Counter recipes, we looked at ways to summarize data. These recipes showed how to compute a central value, as well as variance and extrema.
Another common statistical summary involves the degree of correlation between two sets of data. This is not directly supported by Python's standard library.
One commonly used metric for correlation is called Pearson's r. The r-value is number between -1 and +1 that expresses the probability that the data values will correlate with each other.
A value of zero says the data is random. A value of 0.95 suggests that 95% of the values correlate, and 5% don't correlate well. A value of -.95 says that 95% of the values have an inverse correlation: when one variable increases, the other decreases.
How can we determine if two sets of data correlate?
Getting ready
One expression for Pearson's r is this:
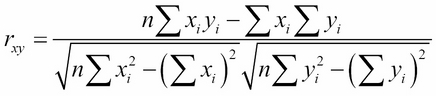
This relies on a large number of individual summations...
























































