Traditional model synchronization on monitors
Concurrency scenarios occur when you have two or more operations that are executed in parallel one with another. This parallelism can be either true parallelism or simulated parallelism. True parallelism is when your application is executed in parallel on two different CPU cores, like so:
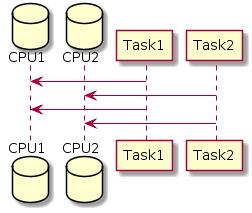
Simulated parallelism is when all of your parallel tasks are executed on the same processor core, however the processor switches from one task to another from time to time. Every task is composed of so-called atomic actions—smallest tasks that cannot be interrupted until they complete. The processor can take a certain amount of atomic actions from one task, and then execute a certain number of atomic tasks from another task:
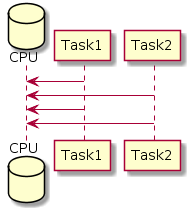
When you are writing a parallel application, you will often come across a situation where your tasks need to communicate one with another. One such situation when this may happen is when your concurrent tasks need to access some kind of...


































































