Linked lists
Linked lists, as the name suggests, consists, of data items (nodes) that are linked to one another by means of pointers. Basically, there are two types of linked lists:
- Linked list: This is where each node has a pointer to the following node
- Doubly linked list: This is where each node has a pointer to the following and previous nodes
The following diagram illustrates the difference:
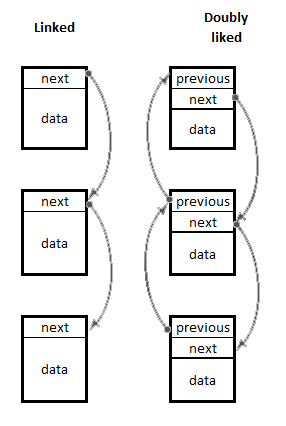
Linked lists of both types may be addressed in a few ways. Obviously, there is at least a pointer to the first node of the list (called top), which is optionally accompanied by a pointer to the last node of the list (called tail). There is, of course, no limit to the amount of auxiliary pointers, should there be a need for such. Pointer fields in the nodes are typically referred to as next and previous. As we can see in the diagram, the last node of a linked list and the first and the last nodes of a doubly linked list have next, previous, and next fields that point nowhere-such pointers are considered...






























































