DC motor speed control - PWM method
In this section, an important fundamental known as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) will be introduced. So far in the examples, the analogRead() and analogWrite() functions were used with the analog I/O pins. However, for achieving PWM, the new thing that we will do is to use the analogWrite() function to send signals on digital pin 3. We will only change the C sketch slightly and retain the same circuit that was setup during the previous example; but before that let us quickly understand PWM.
A signal (or pulse) is basically represented by a voltage level on a particular pin spanning for a certain amount of time (known as the width of the signal/pulse). Being an advanced topic, only the bare minimum required fundamentals will be discussed here. The speed of a motor is controlled by regulating the input voltage to the motor. Conventionally, impedance (resistance) is used to regulate the input voltage and control the speed of motors.
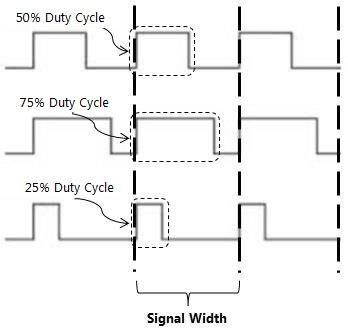
Figure 2: Pulse Width Modulation...




































































