Introduction to monitor refresh rates
These days, flat screen Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) monitors are very common. However, to understand refresh rates and double buffering, we need to understand how older monitors display an image. Along the way, we will learn about common graphics terms, such as pixels and screen resolution:
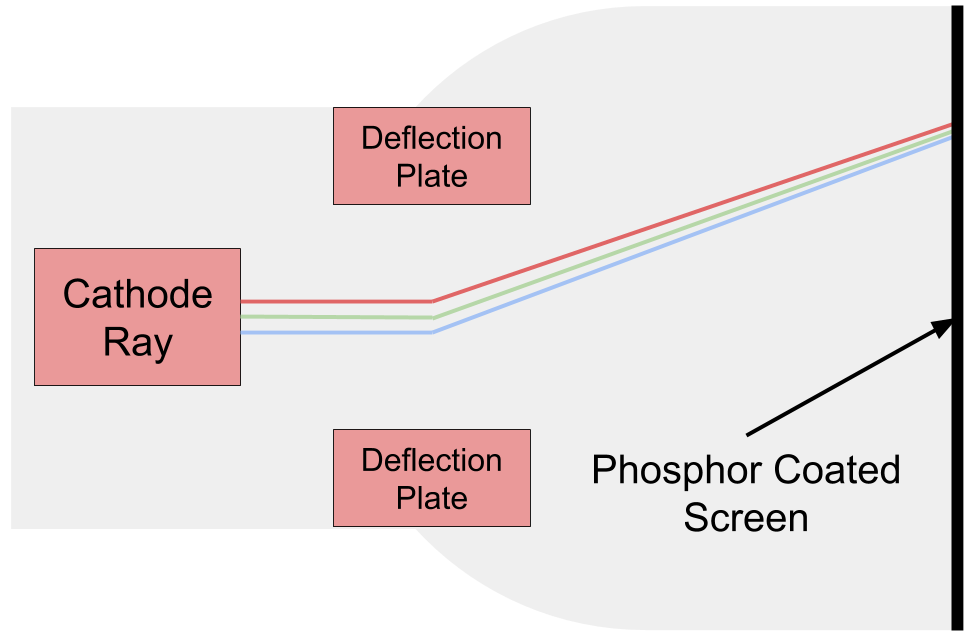
Figure 11.1 - Simplified cathode ray tube diagram
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) monitors contain screens with millions of tiny red, green, and blue phosphor dots. These dots glow for a short time when struck by an electron beam that travels across the screen to create an image. The cathode is a heated filament inside a vacuum sealed glass tube. The ray is a stream of electrons generated by an electron gun, which is directed by magnetic deflection plates. By adjusting the magnetic field of the plates, the electron beam can be moved around and adjusted to strike every part of the screen.
The screen is coated with phosphor, an organic material that glows for a short time when...




























































