1.11 Qubits
In the first section of this chapter, we looked at data. Starting with the bits 0 and 1, we built integers, and I indicated that we could also represent floating-point numbers. Let’s switch from the arithmetic and algebra of numbers to geometry.
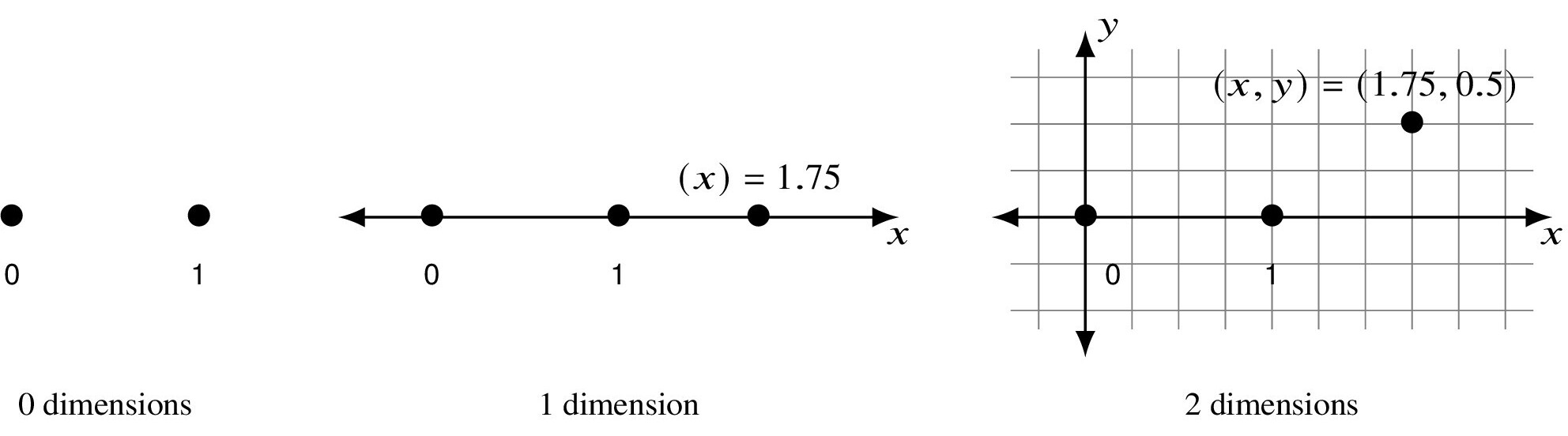
A single point is 0-dimensional. Two points are just two 0-dimensional objects. Let’s label these points 0 and 1. When we draw an infinite line through the two points and consider all the points on the line, we get a 1-dimensional object. We can represent each such point as (x), or just x, where x is a real number. If we have another line drawn vertically and perpendicular to the first, we get a plane. A plane is 2-dimensional, and we can represent every point in it with coordinates (x, y). The point (0, 0) is the origin.
This is the...































































