Using SciPy in Jupyter
SciPy is an open source library for mathematics, science and, engineering. With such a wide scope, there are many areas we can explore using SciPy:
- Integration
- Optimization
- Interpolation
- Fourier transforms
- Linear algebra
- There are several other intense sets of functionality as well, such as signal processing
Using SciPy integration in Jupyter
A standard mathematical process is integrating an equation. SciPy accomplishes this using a callback function to iteratively calculate out the integration of your function. For example, suppose that we wanted to determine the integral of the following equation:
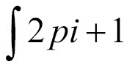
We would use a script like the following. We are using the definition of pi from the standard math package.
from scipy.integrate import quadimport mathdef integrand(x, a, b): return a*math.pi + ba = 2b = 1quad(integrand, 0, 1, args=(a,b))
Again, this coding is very clean and simple, yet almost impossible to do in many languages. Running this script in Jupyter we see the results...





































































