Implementing "there exists" processing
The processing patterns we've been looking at can all be summarized with the quantifier for all. It's been an implicit part of all of the processing definitions:
Map: For all items in the source, apply the map function. We can use the quantifier to make this explicit: {M(x) ∀ x: x ∈ C}
Filter: For all items in the source, pass those for which the filter function is
true. Here also, we've used the quantifier to make this explicit. We want all values, x, from a set, C, if some function, F(x), istrue: {x ∀ x: x ∈ C if F(x)}- Reduce: For all items in the source, use the given operator and base value to compute a summary. The rule for this is a recursion that clearly works for all values of the source collection or iterable:
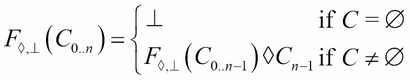 .
.
We've used the notation C0..n in the Pythonic sense of an open-ended range. Values with index positions of 0 and n-1 are included, but the value at index position n is not included. This means that there are no elements in this range.
What...
























































