About Java programming
Java is a general-purpose computer programming language that is concurrent, class-based, and object-oriented. It includes the following functionalities:
Real-world programming
Reusability (reuse of components once created)
Modularity (modifying a required object without affecting the functionality of the other object)
Resilience to change (redefining the system without any major change in other parts)
Information hiding (limited access to information can be given to the user, resulting in security in a program)
How does Java work?
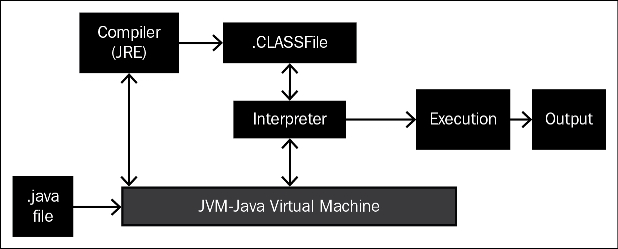
Java programs are written in
.javafiles.When the
.javafile is executed, Java Virtual Machine (JVM) will interact with one of its components, Compiler, which will convert the.javafile to a.classfile.Interpreter is another component of Java Virtual Machine that will interact with the
.classfile in runtime, that is, at the time of execution, and this provides the output.Note
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) + JRE (Java Runtime Environment) = JDK (Java Development Kit)
Package
A package is a collection of classes and interfaces that provides a high-level layer of access protection and namespace management.
At a high level, its a folder where the Java classes are placed.
Class
A class defines the structure and behavior of an object or set of objects.
Objects
Objects are the basic building blocks of the OOP, and they can also be defined as an instance of a class.
Objects have the following characteristics:
State: The state of an object is indicated by a set of attributes and the values of these attributes.
Behavior: The behavior of an object refers to the change of its state over a period of time.
Identity: Each object has a unique identity for identification.
A class in the object-oriented methodology is a collection of various attributes, such as data and methods. You can access the data of a class using its methods.
Note
The
Mainmethod is the entry point of execution in a Java program.
Importing the sample Java project in the Eclipse workspace
The following are the steps to run the sample programs:
Launch Eclipse.
Import the project (File | Import | Existing Project | Java project path)
MySampleJavaProjectas an existing project.Enable the Navigator view on Eclipse (from Window Tab | Show View).
Right-click on the
.javafile and select Run as Java Application.
A simple Java program example
The following is an example of a Java program:
package pckg1;
public class example1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("I am done with my 1st program on java");
}
}The output for the preceding code will be as follows:
I am done with my 1st program on java
























































