Hardware configuration
We are now going to assemble the different parts of this project. First, you need to get familiar with the different pins of the SHT10 sensor:
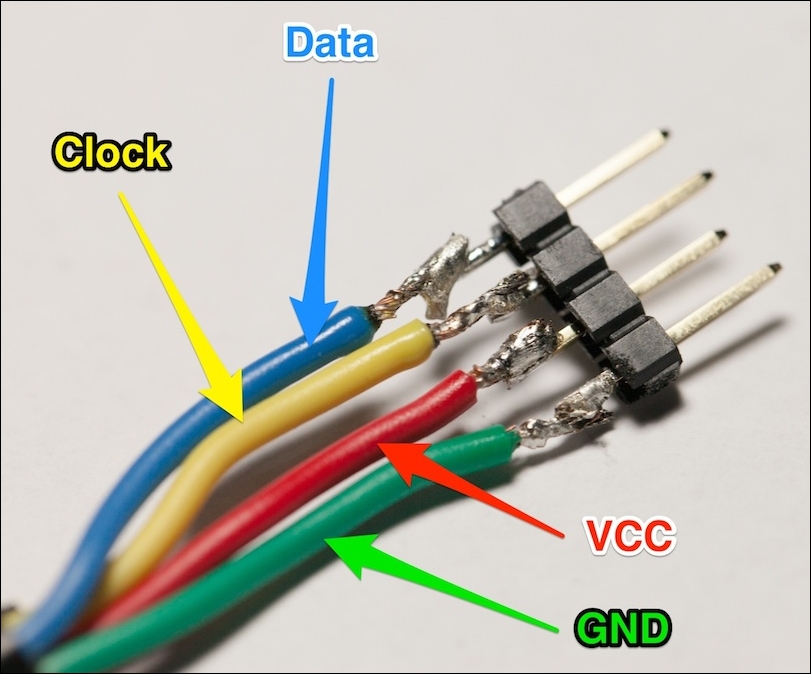
Once that's done, put the sensor's connector on the breadboard. Also connect the VCC and GND pins of the ESP8266 to the breadboard red and blue power lines.
Next, connect the sensor's VCC and GND pins to the red and blue power rails, respectively. Then, connect the data pin to pin number 4 of the ESP8266, and the clock pin to pin number 5. Finally, add the 10K Ohm pull-up resistor between the data and the VCC pins of the sensor.
For the relay, simply connect GND to the blue power rail, VCC to the red one, and finally the SIG pin to pin number 15 of the ESP8266.
This is the final result:
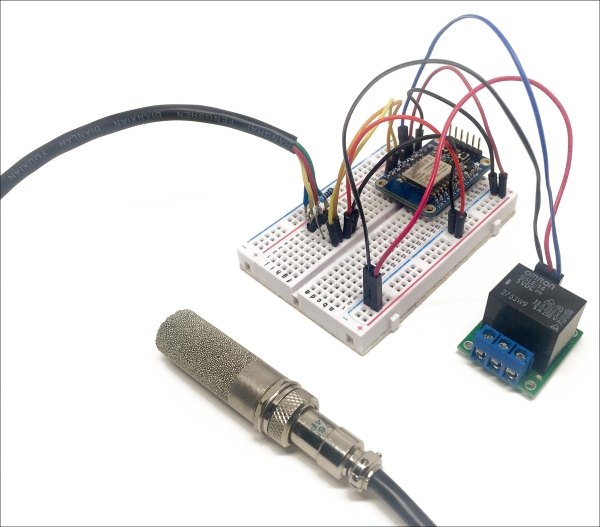
However, we are not done yet; we need something to measure! You can now insert the sensor inside the soil, for example in the pot of a plant inside your home, or in your garden outside. This is how I inserted it to monitor one of the plants in my...
























































