Understanding Spring modules
Spring provides a modular architecture that is one of the most important reasons for the popularity of the Spring Framework. Its layered architecture enables integration of other frameworks easily and without hassle. These modules provide everything that a developer may need to use in enterprise application development. The Spring Framework is organized into 20 different modules that are built on the top of its Core Container.
The following diagram illustrates different Spring modules organized in a layered architecture:
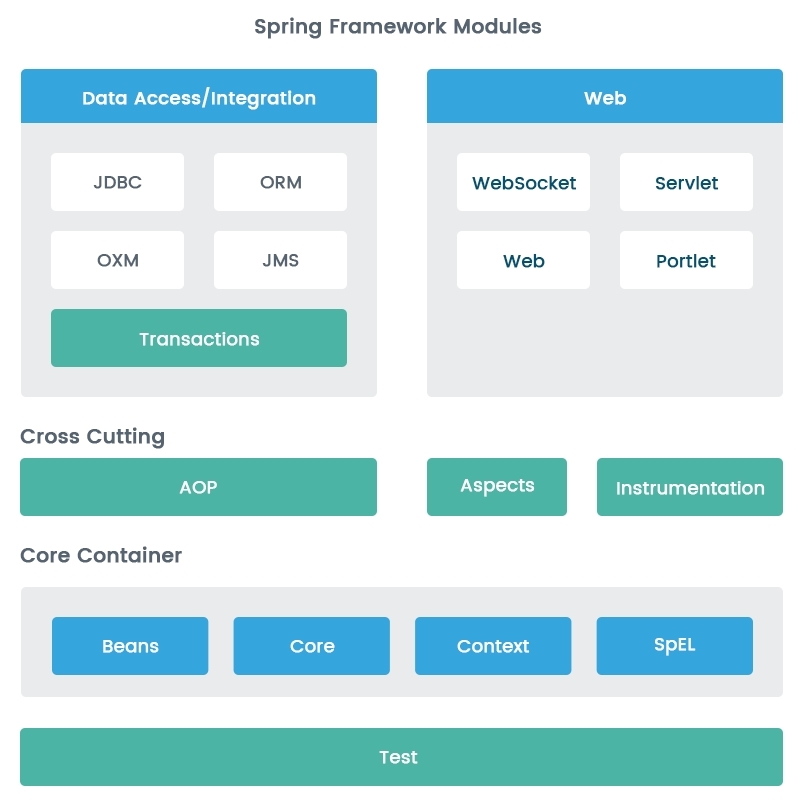
Spring Framework modules
We will start with discussing the Core Container before moving on to other modules.
Core Container
The Spring Core Container provides the core features of the Spring Framework, namely as Core, Beans, Context, and Expression Language, the details of which are as follows:
Artifact | Module Usage |
| This module facilitates all the utilities used by other modules and it also provides a way for managing the different bean life cycle operations. |
| This module is mainly used to decouple code dependencies from your actual business logic and eliminates the use of singleton classes using DI and IoC features. |
| This module provides features like internationalization, and resource loading, and also underpins Java EE features like EJB, JMS, and remoting. |
| This module provides support for accessing properties of beans at runtime and also allows us to manipulate them. |
Crosscutting concerns
Crosscutting concerns are applicable to all the layers of an application, including logging and security, among others. Important Spring modules related to crosscutting concerns are as follows:
Artifact | Module Usage |
| This module is mainly used to perform the tasks which are common amongst different parts of a system like transaction management, logging, and security. To enable this we can implement method-interceptors and pointcuts. |
| This module is used to integrate any custom object type. It is possible using AspectJ, and the main use of this module is to integrate the objects which are not in the control of the container. |
| This module is used to measure the application's performance and also helps to perform error diagnosis using trace information. |
| This module is used to integrate testing support in a Spring application. |
Data Access/Integration
The Data Access/Integration layer in applications interacts with the database and/or the external interfaces. It consists of JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS, and Transaction modules. These modules are spring-jdbc, spring-orm, spring-oxm, spring-jms, and spring-tx.
Web
The Web layer contains the Web, Web-MVC, Web-Socket, and other Web-Portlet modules. The respective module names are spring-web, spring-webmvc, spring-websocket, spring-webmvc-portlet.
In the next section, we will go through different kinds of Spring projects.





































































