Removing all stopped containers
We can remove all stopped containers with a single command. In this recipe, we'll create a bunch of containers in a stopped state, and then delete all of them.
Getting ready
Ensure that Docker daemon 1.13 (and above) are running on the host and can be connected through the Docker client. You will also need some containers in a stopped or running state in order to delete them.
How to do it...
Use the following command:
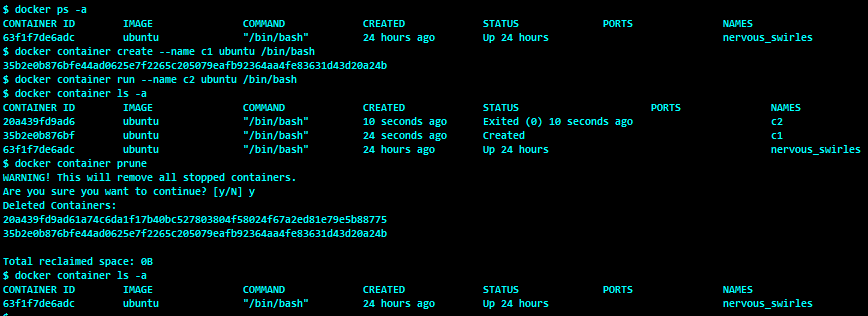
$ docker container prune [OPTIONS]Let's first create a container, and then delete it using the following commands:
$ docker container create --name c1 ubuntu /bin/bash$ docker container run --name c2 ubuntu /bin/bash$ docker container prune
There's more...
By default, the docker container prune command confirms prompts the user for confirmation before removing containers that are not in a running state.
You could avoid the aforementioned confirmation by using the -f or --force option of the docker container prune command.
How it works...
The Docker daemon...




































































