The transmission control protocol
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol used by several application-layer protocols to ensure data delivery without any loss of information during transition, based on sequence and acknowledgment numbers. TCP ensures fail-proof delivery of packets between nodes. TCP sits in between the network layer and the application layer and uses the IP datagram to transfer data packets between the sender and receiver.
The Three-Way Handshake process takes place before the data transfer happens. A TCP connection is like a two-way communication process where not only the sender is actively involved, but even the receiver sends acknowledgments to make it a reliable form of connection.
Understanding the TCP header and its various flags
The TCP header is normally 20 bytes long, but at times, due to the presence of the Options field, the TCP header size can vary up to 60 bytes. The following is an illustration of a simplified TCP header:
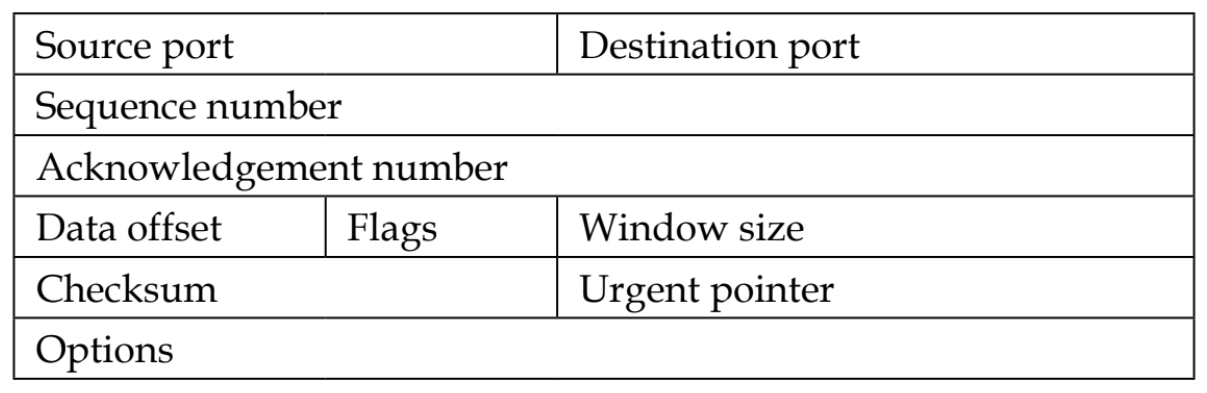
The following is a brief explanation for...




































































