Processing unstructured data
Unstructured data does not lend itself to most of the programming tasks. It has to be processed in various different ways as applicable, to be able to serve as an input to any machine learning algorithm or for visual analysis. Broadly, the unstructured data analysis can be viewed as a series of steps as shown in the following diagram:
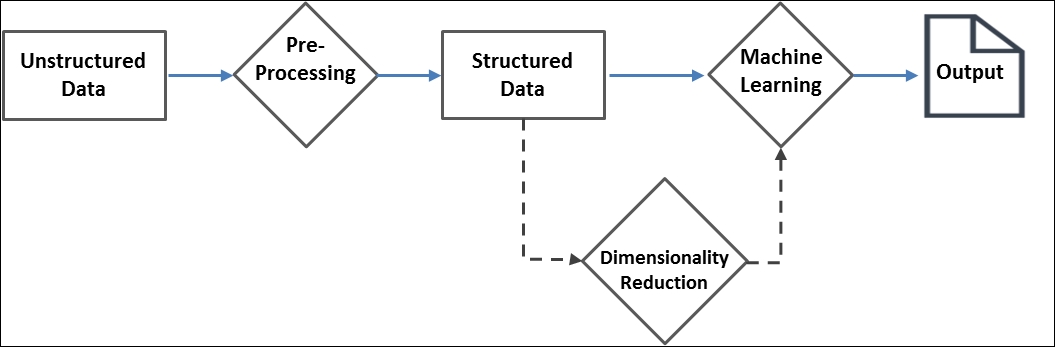
Data pre-processing is the most vital step in any unstructured data analysis. Fortunately, there have been several proven techniques accumulated over time that come in handy. Spark offers most of these techniques out of the box through the ml.features package. Most of the techniques aim to convert text data to concise numerical vectors that can be easily consumed by machine learning algorithms. Developers should understand the specific requirements of their organizations to arrive at the best pre-processing workflow. Remember that better, relevant data is the key to generate better insights.
Let us explore a couple of examples that...



























































