The secant method
The secant method uses secant lines to find the root. A secant line is a straight line that intersects two points of a curve. In the secant method, a line is drawn between two points on the continuous function such that it extends and intersects the 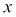 axis. This method can be thought of as a Quasi-Newton method. By successively drawing such secant lines, the root of the function can be approximated.
axis. This method can be thought of as a Quasi-Newton method. By successively drawing such secant lines, the root of the function can be approximated.
The secant method is graphically represented in the following screenshot. An initial guess of the two 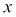 axis values
axis values 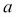 and
and 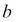 is required to find
is required to find 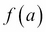 and
and 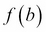 . A secant line y is drawn from
. A secant line y is drawn from 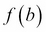 to
to 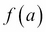 and intersects at point
and intersects at point 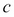 on the
on the 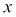 axis such that:
axis such that:
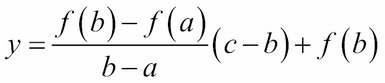
The solution to 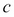 is therefore:
is therefore:
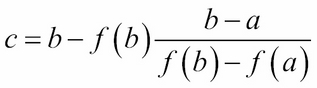
On the next iteration, 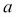 and
and 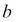 will take on the values of
will take on the values of 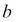 and
and 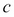 respectively. The method repeats itself, drawing secant lines for the
respectively. The method repeats itself, drawing secant lines for the 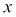 axis values of
axis values of 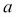 and
and 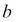 ,
, 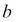 and
and 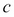 ,
, 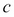 and
and 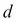 , and so on. The solution terminates when the maximum number of iterations has been reached or the difference between
, and so on. The solution terminates when the maximum number of iterations has been reached or the difference between 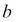 and
and 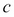 has reached a prespecified tolerance...
has reached a prespecified tolerance...



























































