Routing
For the most part, pfSense does routing transparently. If a node on the local network is attempting to send a packet to a node on a local network, pfSense will send it to the right network, assuming that the network is directly attached to pfSense. If a node on the local network is attempting to send a packet to a remote network, pfSense will send it to a gateway. There are some special cases, however, and we will discuss them in this section.
Static routes
When we have local networks that are reachable through a router other than pfSense's default gateway, we need to configure a static route. A simple example of this situation is a router that is connected to the LAN network. The following diagram illustrates this scenario:
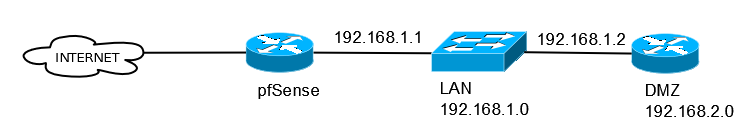
The DMZ network is not directly connected to pfSense and thus requires a static route
In this scenario, the LAN interface has a static IP address of 192.168.1.1. The DMZ router is connected to the LAN switch and DMZ's WAN interface has an IP address of 192.168.1...




































































