Chapter 8. SPI Device Drivers
A Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is (at least) a four-wire bus: Master Input Slave Output (MISO); Master Output Slave Input (MOSI); Serial Clock (SCK); and Chip Select (CS), which is used to connect a serial flash, AD/DA converter. The master always generates the clock. Its speed can reach up to 80 MHz, even if there is no real speed limitation (much faster than I2C as well). The same goes for the CS line, which is always managed by the master.
Each of these signal names has a synonym:
- Whenever you see SIMO, SDI, DI, or SDA, they refer to MOSI.
- SOMI, SDO, DO, and SDA will refer to MISO.
- SCK, CLK, and SCL will refer to SCK.
- S̅ S̅ is the slave select line, also called the CS. CSx can be used (where x is an index, CS0, CS1); EN and ENB can be used too, meaning enable. The CS is usually an active low signal:
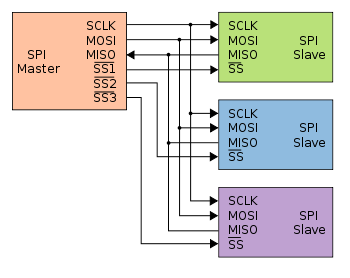
SPI topology (image from Wikipedia)
This chapter will walk through SPI driver concepts such as:
- SPI bus description
- Driver architecture and data structure descriptions...

































































