Scala traits
The trait function in Scala defines a set of features that can be implemented by classes. A trait interface is similar to an interface in Java.
The trait function can be partially implemented, forcing the user (class) of trait to implement the details.
By way of an example, we could have this code:
trait Color {
def isRed(): Boolean
}
class Red extends Color {
def isRed() = true
}
class Blue extends Color {
def isRed() = false
}
var red = new Red();
var blue = new Blue();
red.isRed()
blue.isRed()
The code creates a trait called Color, with one partially implemented function, isRed. So, every class that uses Color will have to implement isRed().
We then implement two classes, Red and Blue, that extend the Color trait (this is the Scala syntax for using trait). Since the isRed() function is partially implemented, both classes have to provide implementations for the trait function.
We can see how this operates in the following Notebook display:
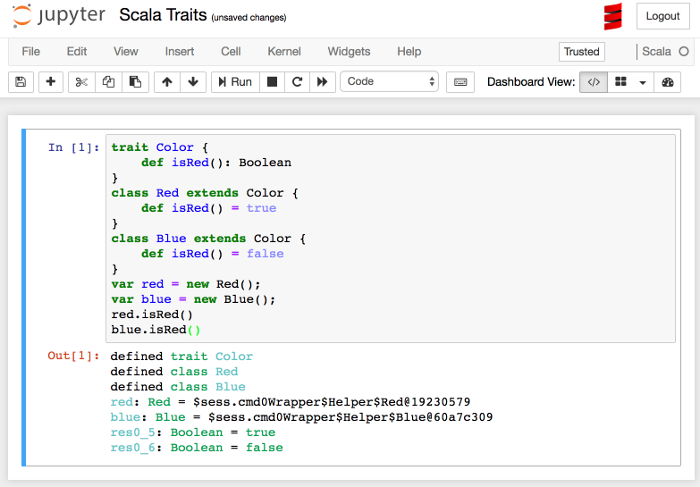
We see (in the output section at the...































































