Setting up the Kubernetes cluster on Windows by minikube
By nature, Docker and Kubernetes are based on a Linux-based OS. Although it is not ideal to use the Windows OS to explore Kubernetes, many people are using the Windows OS as their desktop or laptop machine. Luckily, there are a lot of ways to run the Linux OS on Windows using virtualization technologies, which makes running a Kubernetes cluster on Windows machines possible. Then, we can build a development environment or do a proof of concept on our local Windows machine.
You can run the Linux VM by using any hypervisor on Windows to set up Kubernetes from scratch, but using minikube (https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube) is the fastest way to build a Kubernetes cluster on Windows. Note that this recipe is not ideal for a production environment because it will set up a Kubernetes on Linux VM on Windows.
Getting ready
To set up minikube on Windows requires a hypervisor, either VirtualBox (https://www.virtualbox.org) or Hyper-V, because, again, minikube uses the Linux VM on Windows. This means that you cannot use the Windows virtual machine (for example, running the Windows VM on macOS by parallels).
However, kubectl , the Kubernetes CLI, supports a Windows native binary that can connect to Kubernetes over a network. So, you can set up a portable suite of Kubernetes stacks on your Windows machine.
The following diagram shows the relationship between kubectl, Hypervisor, minikube, and Windows:
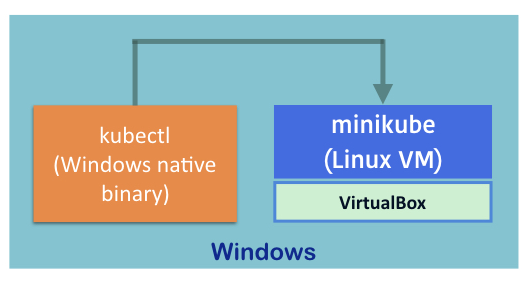
Hyper-V is required for Windows 8 Pro or later. While many users still use Windows 7, we will use VirtualBox as the minikube hypervisor in this recipe.
How to do it...
First of all, VirtualBox for Windows is required:
- Go to the VirtualBox website (https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads) to download the Windows installer.
- Installation is straightforward, so we can just choose the default options and click
Next:

- Next, create the
Kubernetesfolder, which is used to store the minikube and kubectl binaries. Let's create thek8sfolder on top of theC:drive, as shown in the following screenshot:

- This folder must be in the command search path, so open
System Properties, then move to theAdvancedtab. - Click the
Environment Variables...button, then choosePath, and then click theEdit...button, as shown in the following screenshot:

- Then, append
c:\k8s, as follows:

- After clicking the
OKbutton, log off and logo on to Windows again (or reboot) to apply this change. - Next, download minikube for Windows. It is a single binary, so use any web browser to downloadhttps://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases/download/v0.26.1/minikube-windows-amd64 and then copy it to the
c:\k8sfolder, but change the filename tominikube.exe.
- Next, download kubectl for Windows, which can communicate with Kubernetes. It is also single binary like minikube. So, downloadhttps://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.10.2/bin/windows/amd64/kubectl.exe and then copy it to the
c:\k8sfolder as well. - Eventually, you will see two binaries in the
c:\k8sfolder, as shown in the following screenshot:

Note
If you are running anti-virus software, it may prevent you from running kubectl.exe and minikube.exe. If so, please update your anti-virus software setting that allows running these two binaries.
How it works...
Let's get started!
- Open Command Prompt and then type
minikube start, as shown in the following screenshot:

- minikube downloads the Linux VM image and then sets up Kubernetes on the Linux VM; now if you open VirtualBox, you can see that the minikube guest has been registered, as illustrated in the following screenshot:

- Wait for a few minutes to complete the setup of the Kubernetes cluster.
- As per the following screenshot, type
kubectl versionto check the Kubernetes master version. - Use the
kubectl get nodescommand to check whether the Kubernetes node is ready or not:

- Now you can start to use Kubernetes on your machine! Again, Kubernetes is running on the Linux VM, as shown in the next screenshot.
- Using
minikube sshallows you to access the Linux VM that runs Kubernetes:

Therefore, any Linux-based Docker image is capable of running on your Windows machine.
- Type
minikube ipto verify which IP address the Linux VM uses and alsominikube dashboard, to open your default web browser and navigate to the Kubernetes UI ,as shown in the following screenshot:

- If you don't need to use Kubernetes anymore, type
minikube stopor open VirtualBox to stop the Linux guest and release the resource, as shown in the following screenshot:

See also
This recipe describes how to set up a Kubernetes cluster on your Windows OS using minikube. It is the easiest way to start using Kubernetes. It also describes kubectl, the Kubernetes command-line interface tool, which is the entry point form which to control your Kubernetes.





































































