Shared Key Authentication
SKA uses a shared secret such as the WEP key to authenticate the client. The exact exchange of information is illustrated in the following screenshot (taken from www.netgear.com):
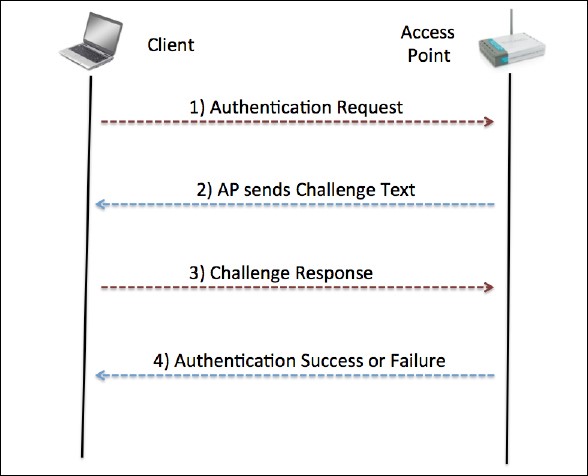
The wireless client sends an authentication request to the access point, which responds back with a challenge. The client now needs to encrypt this challenge with the shared key and send it back to the access point, which decrypts this to check whether it can recover the original challenge text. If it succeeds, the client successfully authenticates; if not, it sends an authentication failed message.
The security problem here is that an attacker passively listening to this entire communication by sniffing the air has access to both the plain text challenge and the encrypted challenge. He can apply the XOR operation to retrieve the keystream. This keystream can be used to encrypt any future challenge sent by the access point without needing to know the actual key.
The most common form of shared...





































































