BFS versus DFS
In this section, we'll look at the differences between the DFS and BFS algorithms. We will compare these differences in terms of various factors.
Order of traversal
In DFS, preference is given to child nodes, which means that after node a and node b are explored, and after node b and node c are explored, we hit a dead end and we backtrack to the previous level. This means that we go back to node b, and then to its next child, which is node c.
In BFS, the nodes are covered level by level, and preference is given to siblings. This means that after node a, nodes b and e are explored, and after that, nodes c, d, and f are explored, as indicated by the following diagram:
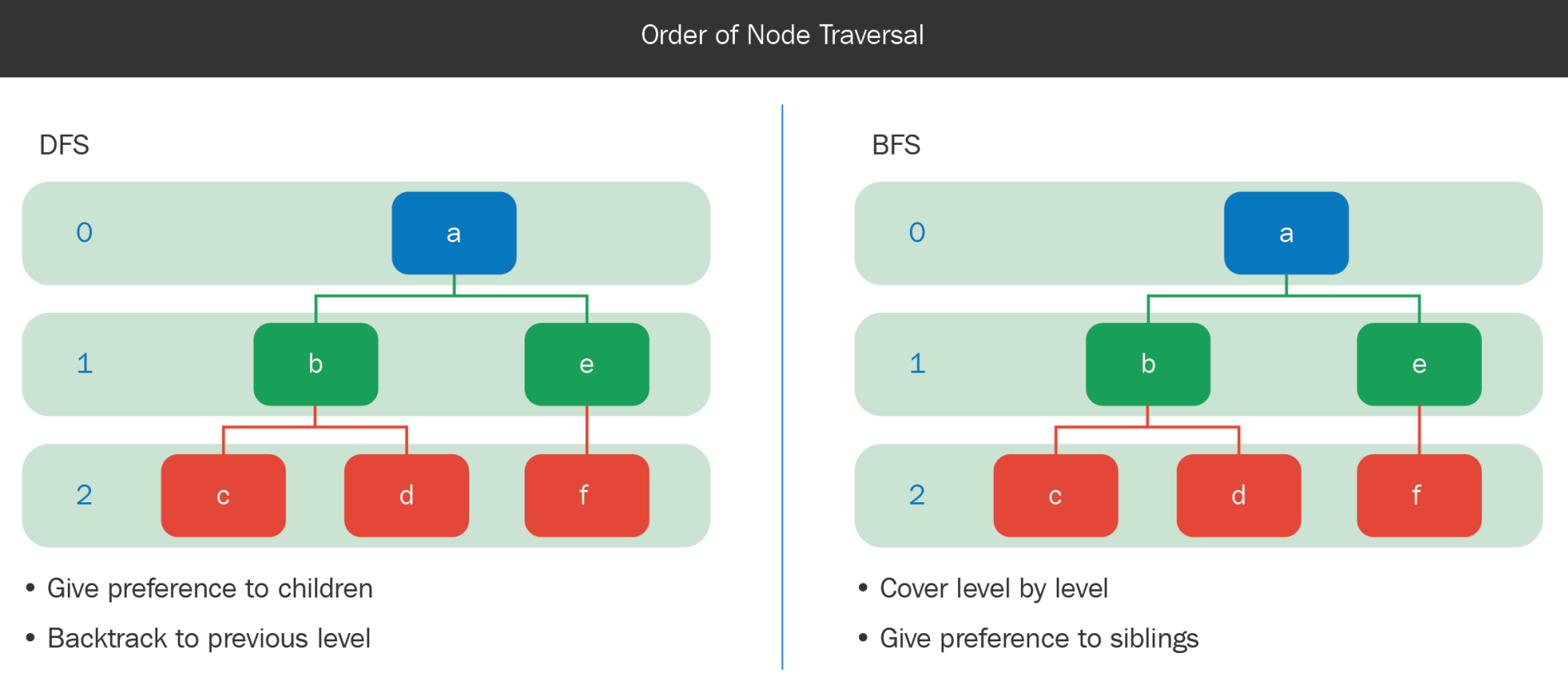
Figure 16
Data structures
In DFS, a stack data structure is used, while in BFS, a queue is used, as shown in the following diagram:
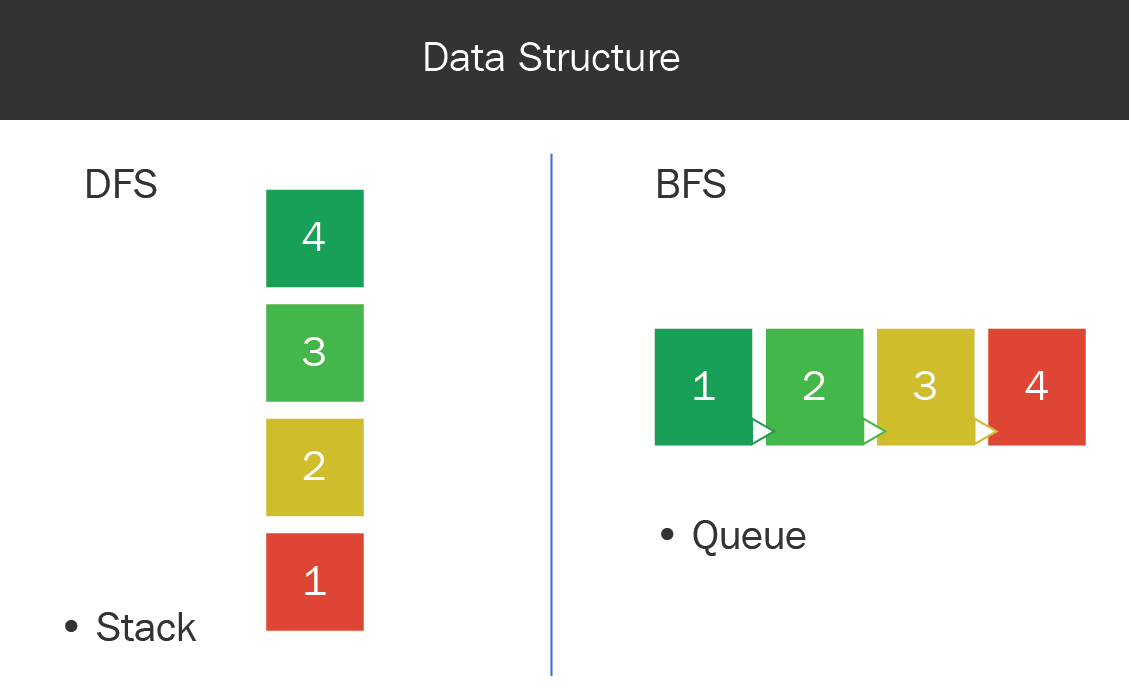
Figure 17
Memory
When recursive DFS is called on node c, the implicit stack stores two entries—one for node e, and one for nodes c and d. So, the memory used is in the order of d, where d is...































































