The BlazingDB team announced a new and free version of BlazingDB’s query execution engine for RAPIDS open-source software by NVIDIA, called BlazingSQL, yesterday.
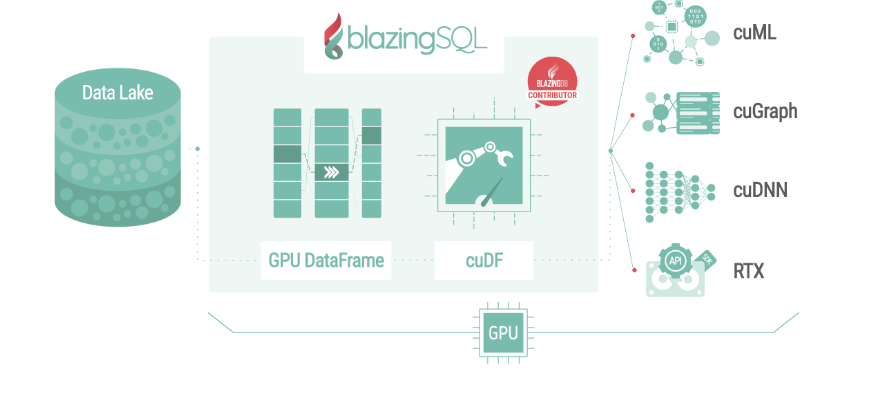
BlazingSQL provides query datasets from enterprise Data Lakes directly into GPU memory as a GPU DataFrame (GDF). GPU DataFrame (GDF) is a project that offers support for interoperability between GPU applications. It also defines a common GPU in-memory data layer.
To provide this data lake integration, and to enable SQL queries on the software, critical open-source libraries were built inside the RAPIDS open-source software. These libraries were then layered on a series of modules from BlazingDB. GDF provides users with PyGDF or Dask_GDF that offers a simple interface similar to the Pandas DataFrame.
 BlazingSQL
BlazingSQL
Unlock access to the largest independent learning library in Tech for FREE!
Get unlimited access to 7500+ expert-authored eBooks and video courses covering every tech area you can think of.
Renews at $15.99/month. Cancel anytime
BlazingSQL also allows Python developers to execute SQL queries directly on the flat files that exist inside the distributed file systems. Moreover, it comes with cuML and cuDNN that comprises GPU-accelerated machine learning and deep learning libraries using GDFs. The GPU DataFrame offers developers the ability to run complete machine learning workloads inside the GPU memory. This reduces the cost of data exchange between different tools, as well as the transfer overhead over the PCIe bus.
The BlazingDB team has given a demo and binary roadmap for the upcoming BlazingSQL releases. BlazingSQL 0.1 uses PyBlazing connection to execute SQL queries on GDFs loaded by the PyGDF API. It will be releasing in the next couple of weeks before 25th October.
BlazingSQL 0.2 involves the integration of BlazingDB’s FileSystem API. This adds the ability to directly query flat files inside the existing distributed file systems. This will be releasing sometime between 25th October to 8th November.
BlazingSQL 0.3 comprises the integration of the distributed scheduler so SQL queries are fanned out across multiple GPUs and servers. This will be releasing between 8th November and 30th November. Finally, the BlazingSQL 0.4 will have Integration of the distributed, multi-layered cache. The release date for BlazingSQL 0.4 hasn’t been assigned but it is expected to release in 2018.
For more information, check out the official BlazingDB blog post.
Introducing Watermelon DB: A new relational database to make your React and React Native apps highly scalable
MariaDB acquires Clustrix to give database customers ‘freedom from Oracle lock-in’
RxDB 8.0.0, a reactive, offline-first, multiplatform database for JavaScript released!
 United States
United States
 Great Britain
Great Britain
 India
India
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 Canada
Canada
 Russia
Russia
 Spain
Spain
 Brazil
Brazil
 Australia
Australia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Hungary
Hungary
 Romania
Romania
 Denmark
Denmark
 Ireland
Ireland
 Estonia
Estonia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Italy
Italy
 Finland
Finland
 Cyprus
Cyprus
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Latvia
Latvia
 Malta
Malta
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Argentina
Argentina
 Colombia
Colombia
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Norway
Norway
 South Korea
South Korea
 Taiwan
Taiwan
 Turkey
Turkey
 Czechia
Czechia
 Austria
Austria
 Greece
Greece
 Isle of Man
Isle of Man
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Japan
Japan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Egypt
Egypt
 Chile
Chile
 Malaysia
Malaysia














