Embedding a progress bar in a status bar
This topic explains how to embed a progress bar in a panel's status bar, a scenario found in countless user interfaces:
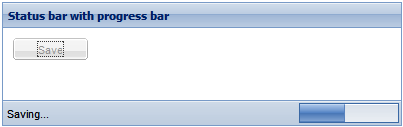
How to do it
- Create a click handler that will simulate a long-running activity and update the progress bar:
Ext.onReady(function() {
var loadFn = function(btn, statusBar) {
btn = Ext.getCmp(btn);
btn.disable();
Ext.fly('statusTxt').update('Saving...');
pBar.wait({
interval: 200,
duration: 5000,
increment: 15,
fn: function() {
btn.enable();
Ext.fly('statusTxt').update('Done');
}
});
};
- Create an instance of the progress bar:
var pBar = new Ext.ProgressBar({
id: 'pBar',
width: 100
});
- Create a host panel and embed the progress bar in the bbar of the panel. Also, add a button that will start the progress bar updates:
var pnl = new Ext.Panel({
title: 'Status bar with progress bar',
renderTo: 'pnl1',
width: 400,
height: 200,
bodyStyle: 'padding:10px;',
items: [{
xtype: 'button',
id: 'btn',
text: 'Save',
width:'75',
handler: loadFn.createCallback('btn', 'sBar')
}],
bbar: {
id: 'sBar',
items: [{ xtype: 'tbtext', text: '',id:'statusTxt' },'->',
pBar]
}
});
How it works
The first step consists of creating loadFn, a function that simulates a long-running operation, so that we can see the progress bar animation when the button is clicked. The heart of loadFn is a call to ProgressBar.wait(…), which initiates the progress bar in an auto-update mode.
And this is how the status bar is embedded in the bbar of the panel:
bbar: {
id: 'sBar',
items: [{ xtype: 'tbtext', text: '',id:'statusTxt' },'->', pBar]
Observe how the progress bar is sent to the rightmost location in the status bar with the help of a Toolbar.Fill instance, declared with '->'.
Creating a custom look for the status bar items
Customizing the look of toolbar items is relatively simple. In this recipe, you will learn how to create toolbar items with a sunken look that can be found in many desktop applications:

How to do it
- Create the styles that will provide the custom look of the status bar text items:
.custom-status-text-panel
{
border-top:1px solid #99BBE8;
border-right:1px solid #fff;
border-bottom:1px solid #fff;
border-left:1px solid #99BBE8;
padding:1px 2px 2px 1px;
}
- Create a host panel:
Ext.onReady(function() {
var pnl = new Ext.Panel({
title: 'Status bar with sunken text items',
renderTo: 'pnl1',
width: 400,
height: 200,
bodyStyle: 'padding:10px;',
- Define the panel's bbar with the text items:
bbar: {
id: 'sBar',
items: [
{ id: 'cachedCount', xtype:'tbtext',
text: 'Cached: 15' }, ' ',
{ id: 'uploadedCount', xtype: 'tbtext',
text: 'Uploaded: 7' }, ' ',
{ id: 'invalidCount', xtype: 'tbtext',
text: 'Invalid: 2' }
]
},
- Now, add a handler for the afterrender event and use it to modify the styles of the text items:
listeners: {
'afterrender': {
fn: function() {
Ext.fly(Ext.getCmp('cachedCount').getEl()).parent().
addClass('custom-status-text-panel');
Ext.fly(Ext.getCmp('uploadedCount').getEl()).parent().
addClass('custom-status-text-panel');
Ext.fly(Ext.getCmp('invalidCount').getEl()).parent().
addClass('custom-status-text-panel');
},
delay:500
}
}
How it works
The actual look of the items is defined by the style in the custom-status-text-panel CSS class. After the host panel and toolbar are created and rendered, the look of the items is changed by applying the style to each of the TD elements that contain the items. For example:
Ext.fly(Ext.getCmp('uploadedCount').getEl()).parent().
addClass('custom-status-text-panel');
See also...
- The previous recipe, Embedding a progress bar in a status bar, explains how a progress bar can be embedded in a panel's status bar
Using a progress bar to indicate that your application is busy
In this topic, you will learn how to use a progress bar to indicate that your application is busy performing an operation. The next screenshot shows a progress bar built using this recipe:

Unlock access to the largest independent learning library in Tech for FREE!
Get unlimited access to 7500+ expert-authored eBooks and video courses covering every tech area you can think of.
Renews at €14.99/month. Cancel anytime
How to do it
- Define the progress bar:
Ext.onReady(function() {
Ext.QuickTips.init();
var pBar = new Ext.ProgressBar({
id: 'pBar',
width: 300,
renderTo: 'pBarDiv'
});
- Add a handler for the update event and use it to update the wait message:
pBar.on('update', function(val) {
//Handle this event if you need to
// execute code at each progress interval.
Ext.fly('pBarText').dom.innerHTML += '.';
});
- Create a click handler for the button that will simulate a long-running activity:
var btn = Ext.get('btn');
btn.on('click', function() {
Ext.fly('pBarText').update('Please wait');
btn.dom.disabled = true;
pBar.wait({
interval: 200,
duration: 5000,
increment: 15,
fn: function() {
btn.dom.disabled = false;
Ext.fly('pBarText').update('Done');
}
});
});
- Add the button to the page:
<button id="btn">Start long-running operation</button>
How it works
After creating the progress bar, the handler for its update event is created. While I use this handler simply to update the text message, you can use it to execute some other code every time that a progress interval occurs.
The click handler for the button calls the progress bar's wait(…) function, which causes the progress bar to auto-update at the configured interval and reset itself after the configured duration:
pBar.wait({
interval: 200,
duration: 5000,
increment: 15,
fn: function() {
btn.dom.disabled = false;
Ext.fly('pBarText').update('Done');
}
});
There's more
The progress bar can also be configured to run indefinitely by not passing the duration config option. Clearing the progress bar in this scenario requires a call to the reset() function.
See also...
- The next recipe, Using a progress bar to report progress updates, illustrates how a progress bar can be set up to notify the user that progress is being made in the execution of an operation
- The Changing the look of a progress bar recipe (covered later in this article) shows you how easy it is to change the look of the progress bar using custom styles
Summary
This article consisted recipes that examined the commonly-used menu items, as well as the different ways of setting up toolbars and progress bars in your applications.
[ 1 | 2 ]
If you have read this article you may be interested to view :
 United States
United States
 Great Britain
Great Britain
 India
India
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 Canada
Canada
 Russia
Russia
 Spain
Spain
 Brazil
Brazil
 Australia
Australia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Hungary
Hungary
 Romania
Romania
 Denmark
Denmark
 Ireland
Ireland
 Estonia
Estonia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Italy
Italy
 Finland
Finland
 Cyprus
Cyprus
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Latvia
Latvia
 Malta
Malta
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Argentina
Argentina
 Colombia
Colombia
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Norway
Norway
 South Korea
South Korea
 Taiwan
Taiwan
 Turkey
Turkey
 Czechia
Czechia
 Austria
Austria
 Greece
Greece
 Isle of Man
Isle of Man
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Japan
Japan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Egypt
Egypt
 Chile
Chile
 Malaysia
Malaysia
















