(For more resources related to this topic, see here.)
Employee Recruitment Management System basics
Hiring the right candidate is a challenge for the recruitment team of any company. The process of hiring candidates can differ from company to company. Different sources such as job sites, networking, and consulting firms can be used to get the right candidate, but most companies prefer to hire a candidate from their own employee network. Before starting the hiring process, a recruiter should have a proper understanding of the candidate profile that fits the company's requirements.
Normally, this process starts by screening candidate resumes fetched from different sources. Once they have resumes of appropriate candidates, the recruitment team starts working on resumes one by one. Recruiters talk to potential candidates and enquire about their skills and test their interpersonal skills. Recruiters play an important role in the hiring process; they prepare candidates for interview and provide interview feedback.
Employee Recruitment Management System design
In the employee recruitment applications, we will be using the key objects shown in the following figure to capture the required information:

The blocks perform the following tasks:
- Company: This block stores the company details
- Candidate: This block stores information about the candidate profile
- Employee: This block stores employee data
- CRM User : This block stores Microsoft CRM user information
As we are going to use Microsoft CRM 2011 as a platform to build our application, let's map these key blocks with Microsoft CRM 2011 entities:
- Company: The term "account" in Microsoft CRM represents an organization, so we can map the company object with an account entity and can store company information in the account entity.
- Candidate: The Candidate object will store information about suitable candidates for our company. We will use the candidate entity to store all interview related feedback, other position details, and address information. We are going to map the candidate entity with a lead entity, because it has most of the fields OOB that we need for our candidate entity.
- Employee: In Microsoft CRM 2011 sales process, when lead is qualified, it is converted to an account, a contact, and an opportunity, so we utilize this process for our application. When a candidate is selected, we will convert the candidate to an employee using the OOB process, which will map all the candidate information to the Candidate entity automatically.
When a lead is converted to an account or contact or opportunity, the lead record is deactivated by Microsoft CRM 2011.
Let's talk about the process flow that we are going to use in our employee recruitment application. Recruiters will start the process of hiring a candidate by importing candidate resumes in Microsoft CRM under the Candidate entity; we will customize our OOB entities to include the required information. Once data is imported in Microsoft CRM, the recruiter will start the screening of candidates one by one. He will schedule Technical, Project Manager, and finally HR rounds. Once the candidate is selected the recruiter will create an offer letter for that candidate, send it to the respective candidate, and convert the Candidate entity to Employee. The following flowchart shows our employee recruitment application process flow:

Data model
We have identified the data model for required entities. We need to customize OOB entities based on the data model tables.
Customizing entities for Employee Recruitment Management System
Once we have the data model ready, we need to customize the Microsoft CRM UI and OOB entities. Let's first create our solution called HR Module and add the required entities to that solution.
Customizing Microsoft CRM UI
We need to customize the Microsoft CRM site map. We have options to modify the sitemap manually or using the site map editor tool. We need to customize the site map based on the following table:
|
Sr No
|
Customization Detail
|
|
1
|
Remove Left Navigation: Marketing, Service, Resource Center
|
|
2
|
Rename Left Navigation: Sales to HR Module, Setting to Configuration
|
|
3
|
Remove Left Navigation items under My Work: Queues, Articles,Announcements
|
|
4
|
Remove all Left Navigation items under HR Module left navigation: except Lead, Accounts , and Contacts
|
After customizing the site map, Microsoft CRM UI should look like the following screenshot:
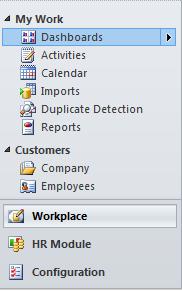
It is recommended that you comment unwanted navigation areas out of the site map instead of removing them.
Customizing OOB entities
After we have customized Microsoft CRM UI, we need to rename the entity and entity views. We also need to perform the following actions:
- Renaming OOB entities: We need to rename the lead, account, and contact entities to candidate, company, and employee. Open the entities in edit mode and rename them.
- Changing Translation labels: After renaming the OOB entities, we need to change the translation labels in Microsoft CRM. We need to convert Lead to Candidate and Contact to Employee.
Creating/customizing entity fields:
We need to create and customize entity fields; based on the data model we just saw, let's create candidate entity fields. Use the following steps to create fields:
- Open our HRModule solution.
- Navigate to Entities | Candidate | Fields.
- Click on New to create a new field.
- Enter the following field properties:
- Display Name: Text that you want to show to the user on the form.
- Name: This will be populated automatically as we tab out from the Display Name field.
The Display Name field is used as a label in Microsoft CRM 2011 entity form and views, whereas the Name field is used to refer to the field in code.
- Requirement Level: Used to enforce data validation on the form.
- Searchable: If this is true, this field will be available in the Advance Finds field list.
- Field Security: Used to enable field-level security. It is a new feature added in Microsoft CRM 2011. Refer to the Setting field-level security in Microsoft CRM 2011 section for more details.
- Auditing: Used to enable auditing for entity fields. It is also a new feature added in Microsoft CRM 2011. Using auditing, we can track entity and attribute data changes for an organization. You can refer to http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg309664.aspx for more details on the auditing feature.
- Description: Used to provide additional information about fields.
- Type: Represents what type of data we are going to store in this field; based on the type selected, we need to set other properties.
You can't change the data type of a created field, but you can change its properties.
After filling in this information, our entity form should look like the following screenshot:

We need to create fields for all entities based on the preceding steps, one by one.
Setting relationship mapping
In Microsoft CRM 2011, we can relate two entities by creating a relationship between them. We can create three types of relationships:
- One-to-many relationship: A one-to-many relationship is created between one primary entity and many related entities. Microsoft CRM 2011 creates a relationship field (lookup field) automatically for each related entity when a one-to-many relationship is created.
We can create a self-relationship by selecting a primary entity on both sides.
- Many-to-one relationship: A many-to-one relationship is created between many related entities and one primary entity.
- Many-to-many relationship: A many-to-many relationship can be created between many related entities. To create a many-to-many relationship, the user must have Append and Append To privileges in both side entities.
We can define different relationship behaviors while creating a relationship; you can refer to http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg309412.aspx for more details.
Unlock access to the largest independent learning library in Tech for FREE!
Get unlimited access to 7500+ expert-authored eBooks and video courses covering every tech area you can think of.
Renews at ₹800/month. Cancel anytime
After creating a relationship, we can define a mapping to transfer values from parent entity to child entity, but this functionality can only achieved when a child entity record is created from a parent entity using the Add New button from the Associated view We need to set up relationship mapping so that we can take the candidate field values to the employee entity when the recruiter converts a candidate into an employee. Use the following steps to set the mapping:
- Navigate to 1:N Relationship under the Candidate entity.
- Open the contact_originating_lead mapping to edit it.
- Navigate to Mapping and click on New to add a mapping.
- Select new_variablecompensation from the Source and Target entities and click on OK.
- Follow step 4 to add mapping for the fields shown in the following screenshot:

Form design
Now we need to design forms for our entity, and we need to remove unnecessary fields from entity forms.
Use the following steps to customize entity forms:
- Open the solution that we created.
- Navigate to Entity | Account | Forms.
- Open the main form to modify it, as shown in the following screenshot:

We can remove unwanted fields easily by selecting them one by one and using the Remove ribbon button on the entity form. To place the field, we just need to drag-and-drop it from the right-hand side field explorer.
Account form design
Once we have customized the account entity, we need to design the account form shown in the following screenshot:

Candidate form design
The candidate form should look like the following screenshot after customization:

Employee form design
After removing unwanted fields and adding required fields, the employee form should look like the following screenshot:

Setting a security model for ERMS
Microsoft CRM provides us the OOB security model that helps us to prevent unauthorized access to our data. We can enforce security in Microsoft CRM using security roles. A security role is a combination of different privileges and access levels.
- Privileges: These are actions such as Create , Write, Delete , Read, Append, Append To, Assign, Share, and Reparent that a Microsoft CRM user can perform on entities. The list of the actions performed is as follows:
- Create : This action is used to create an entity record
- Read: This action is used to read an entity record
- Write: This action is used to modify an entity record
- Delete : This action is used to delete an entity record
- Append: This action is used to relate one entity record to another entity record
- Append To: This action is used to relate other entity records to the current entity record
- Share: This action is used to share an entity record with another user
- Reparent: This action is used to assign a different owner to an entity record
- Access level: This defines on which entity record a Microsoft CRM user can perform actions defined by privileges. We have the following actions under access levels:
- Organization: This action is used to provide access to all records in an organization
- Parent-child Business Unit: This action is used to provide access to all the records in the user's business unit as well as in all child business units of the user's business unit
- Business: This action is used to provide access to all records in the user's business unit
- User: This action allows the user to access records created by him/her, or shared with him/her, or shared with his/her team
We must assign at least one security role to access Microsoft CRM applications. Microsoft CRM provides us with 14 OOB security roles that can be customized based on our requirements. The following diagram is the security-role hierarchy that we have identified for the Employee Management System:

The blocks in the preceding diagram can be explained as follows:
- HR Manager : This role will have access to all information for an employee in the ERMS system
- Recruiter: This role will not have access to information about offered packages to an employee
- System Administrator: This role will have administrative privileges and will be responsible for customizing and maintaining ERMS
We will be customizing the existing security roles for our ERMS . The following table shows the security role mapping that we be will using:
|
Microsoft CRM Security Role
|
ERMS Security Role
|
|
Sales Manager
|
Manager
|
|
Salesperson
|
Salesperson
|
|
System Administrator
|
System Administrator
|
Customizing the existing security role
We need to use the following steps to customize the existing security role:
- Navigation to Setting | Administration | Security Roles.
- Double-click on the Sales Manager role to open it in edit mode.
- Change Role Name to Manager.
- Click on Save and then on Close .
- Follow the same steps to change the name of the Sales Person role to Recruiter.
You can also create a new Manager Security role by copying the Sales Manager role.
Once we have changed the security role name, we need to configure the Security Manager and Recruiter roles to remove unnecessary privileges. Follow the ensuing instructions to configure the Manager Security role:
- Navigate to the Core Records tab in the Manager Security role.
- Clear all privileges from the Opportunity and Document location entities.
- Navigate to the Marketing tab and clear all privileges from the Campaign and Marketing list entities.
- Navigate to the Sales tab and clear all privileges from all sales module entities, as shown in the following screenshot:

- Navigate to the Service tab and clear all privileges from all service module entities.
- Click on Save and Close .
Follow all the preceding steps to remove the same privileges from the Recruiter role as well.
Setting field-level security in Microsoft CRM 2011
Microsoft CRM 2011 contains an OOB feature for field-level security. Using field-level security, we can protect Microsoft CRM form fields from unauthorized access. This feature is only available in custom attributes. You can only apply field-level security to the custom fields of system entities. While creating/modifying fields, you can enable field-level security. The following screenshot shows how we can Enable/Disable the Field Security option:

Once field-level security is enabled, we can set the field-level security profile. Let's apply field-level security in the offered package section in the Candidate entity. We have already enabled field-level security for these three fields under the offered package section in Candidate entity. Use the following steps to set the field-level security profile:
- Navigate to Settings | Administration | Field Security Profiles.
- Click on New to create the new security profile.
- Fill in the following information:
- Name: Recruitment Team Profile
- Description: Security profile for recruitment team
- Click on Save.
- Navigate to Users, under the Members section, in the left-hand navigation.
- Click on Add to add a user from whom you want to secure these fields.
- Navigate to Field Permission under the Common section in the left-hand navigation.
- Select all records and click on the Edit button.
- Select No from all drop-down fields. These fields can be implemented as shown in the following screenshot:

Now all Microsoft CRM users with the Recruitment security role won't be able to see the values in these fields. They won't even be able to set values for these fields.
 United States
United States
 Great Britain
Great Britain
 India
India
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 Canada
Canada
 Spain
Spain
 Brazil
Brazil
 Australia
Australia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Hungary
Hungary
 Romania
Romania
 Denmark
Denmark
 Ireland
Ireland
 Estonia
Estonia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Italy
Italy
 Finland
Finland
 Cyprus
Cyprus
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Latvia
Latvia
 Malta
Malta
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Argentina
Argentina
 Colombia
Colombia
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Norway
Norway
 South Korea
South Korea
 Taiwan
Taiwan
 Turkey
Turkey
 Czechia
Czechia
 Austria
Austria
 Greece
Greece
 Isle of Man
Isle of Man
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Japan
Japan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Egypt
Egypt
 Chile
Chile
 Malaysia
Malaysia

























