Implementing basic statistics
Starting in version 3.4, basic statistical tools were provided to Python. While nowhere near as comprehensive as NumPy, SciPy, Pandas, or the like, they are useful when having to perform simple calculations and not wanting, or having access to, advanced numeric modules.
How to do it...
Note that the import statement is omitted in the following screenshots:
The
mean(data)function returns the normal average of a sequence or iterator:
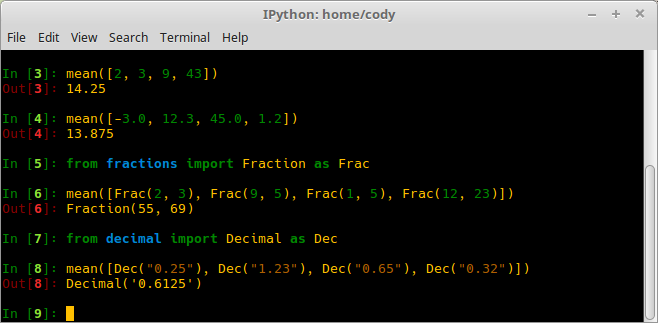
- The line 3 is the mean of integers.
- The line 4 is the mean of floats.
- The lines 6 and line 8 show that fractions can be averaged, as well as decimals.
- The
harmonic_mean(data)function returns the harmonic average of a sequence or iterator. The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the arithmeticmeanof the reciprocals of the argument and is typically used when the average of rates or rations is needed.
For example, if a car traveled for a given distance at 60 mph, then the same distance back at 50 mph, its average speed would be the harmonic...




































































