Decision trees
Decision trees are supervised models that can either preform regression or classification.
Let's take a look at some major league baseball player data from 1986-1987. Each dot represents a single player in the league:
Years (x axis): Number of years played in the major leagues
Hits (y axis): Number of hits the player had in the previous year
Salary (color): Low salary is blue/green, high salary is red/yellow
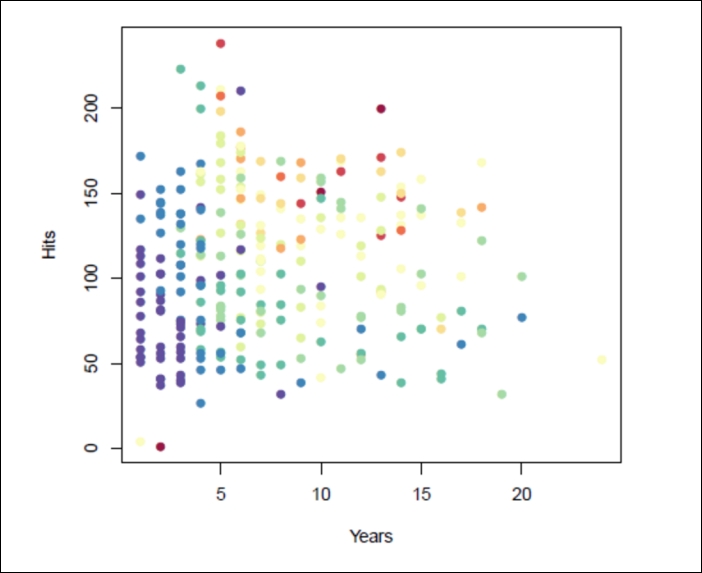
The preceding data is our training data. The idea is to build a model that predicts the salary of future players based on Years and Hits. A decision tree aims to make splits on our data in order to segment the data points that act similarly to each other, but differently to the others. The tree makes multiples of these splits in order to make the most accurate prediction possible. Let's see a tree built for the preceding data:
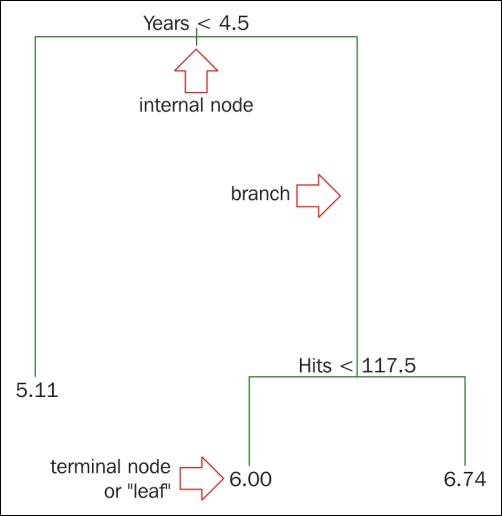
Reading from top to bottom:
The first split is Years < 4.5, when a splitting rule is true, you follow the left branch. When a splitting rule is false...



























































