Using chmod to set permissions on files and directories
chmod, or Change Mode, is a Linux command used to modify the access permissions of files and directories. Everybody wants to keep their data secure and properly organized. For this reason, Linux has the concept of associating an owner and group with every file and directory. These owners and groups have different permissions to access a particular file.
Getting ready
Before we see the use of the chmod command, we need to know that, for different types of users, the symbolic representations that are used are as follows:
uis used for user/ownergis used for groupois used for others
Now, let's create a file named file1.txt to check out the different commands of chmod.
How to do it...
Now, we will see how to use chmod in different ways to set different permissions:
- We first check the current permission of the file and when it was created:
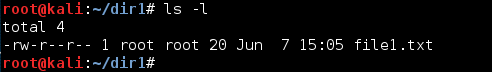
As we can see, currently only the user/owner has read and write permission, whereas groups and other users...





































































