Remindable Actors
Problem
An Actor based application may need to send several messages to an Actor instance. For example, an e-commerce application may require an Actor instance to update the user shopping cart. The Actor instance might be busy completing the process of adding a previous item to the cart. Since, the Actor operations are single threaded, the application will need to wait for the Actor to finish its previous operation to proceed with the next one.
The wait to complete operations degrades performance of application and affects user experience:
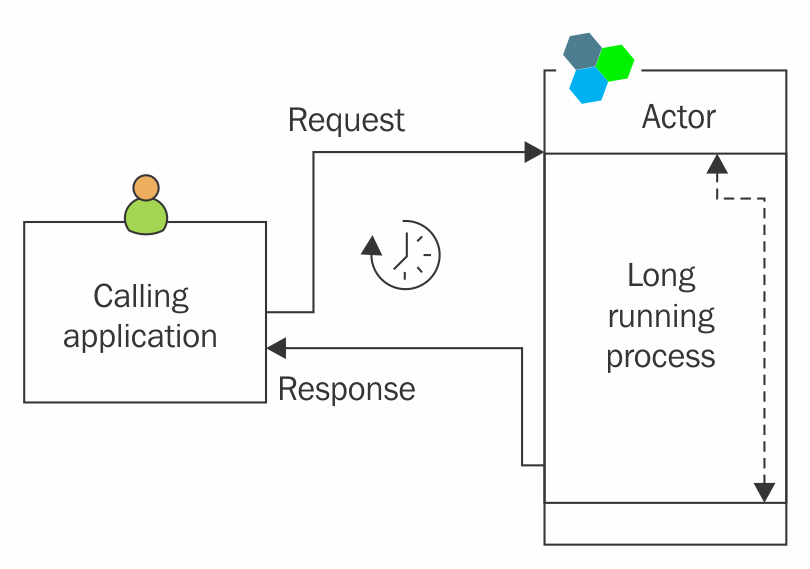
Remindable Actor (Problem)
Solution
All Actors in the system should message themselves when they receive a request. In the above example, the shopping cart Actor can accept the request to add more items to the shopping cart and send a message to itself with the details of item to add to the shopping cart. Once the Actor instance is done processing the previous request, it can consume a message from the queue and add the item to the shopping...




































































