Finite differences in options pricing
Finite difference schemes are very much similar to trinomial tree options pricing, where each node is dependent on three other nodes with an up movement, a down movement, and a flat movement. The motivation behind the finite differencing is the application of the
Black-Scholes Partial Differential Equation (PDE) framework (involving functions and their partial derivatives) whose price 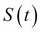 is a function of
is a function of 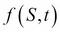 , with
, with 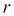 as the risk-free rate,
as the risk-free rate, 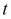 as the time to maturity, and
as the time to maturity, and 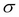 as the volatility of the underlying security:
as the volatility of the underlying security:
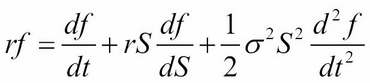
The finite difference technique tends to converge faster than lattices and approximates complex exotic options very well.
To solve a PDE by finite differences working backward in time, a discrete-time grid of size 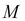 by
by 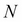 is set up to reflect asset prices over a course of time, such that
is set up to reflect asset prices over a course of time, such that 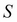 and
and 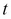 take on the following values at each point on the grid:
take on the following values at each point on the grid:
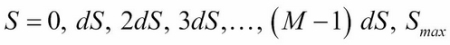
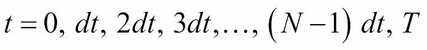
It follows that by grid notation, 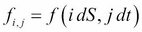 .
. 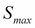 is a suitably large asset price that cannot be reached by the maturity...
is a suitably large asset price that cannot be reached by the maturity...



























































